Page 80 - Bio Engineering Approaches to Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
P. 80
78 CHAPTER 4 Immunotherapy
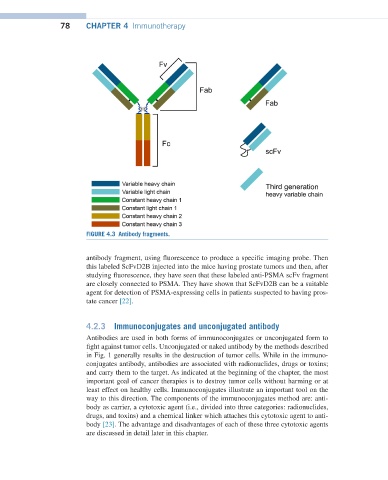
FIGURE 4.3 Antibody fragments.
antibody fragment, using fluorescence to produce a specific imaging probe. Then
this labeled ScFvD2B injected into the mice having prostate tumors and then, after
studying fluorescence, they have seen that these labeled anti-PSMA scFv fragment
are closely connected to PSMA. They have shown that ScFvD2B can be a suitable
agent for detection of PSMA-expressing cells in patients suspected to having pros-
tate cancer [22].
4.2.3 Immunoconjugates and unconjugated antibody
Antibodies are used in both forms of immunoconjugates or unconjugated form to
fight against tumor cells. Unconjugated or naked antibody by the methods described
in Fig. 1 generally results in the destruction of tumor cells. While in the immuno-
conjugates antibody, antibodies are associated with radionuclides, drugs or toxins;
and carry them to the target. As indicated at the beginning of the chapter, the most
important goal of cancer therapies is to destroy tumor cells without harming or at
least effect on healthy cells. Immunoconjugates illustrate an important tool on the
way to this direction. The components of the immunoconjugates method are: anti-
body as carrier, a cytotoxic agent (i.e., divided into three categories: radionuclides,
drugs, and toxins) and a chemical linker which attaches this cytotoxic agent to anti-
body [23]. The advantage and disadvantages of each of these three cytotoxic agents
are discussed in detail later in this chapter.