Page 159 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 159
6.1 Introduction 135
Leloir-GTs utilize sugar nucleotides as activated donor substrates. Sugar moieties
bound to nucleoside mono- or diphosphates, like cytosine monophosphate (CMP),
thymidine diphosphate (dTDP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and the most
common uridine diphosphate (UDP), are transferred by two types of Leloir-GTs.
One class of GTs display an inversion of stereochemistry with regard to the
anomeric center of the transferred sugar resulting in changes from α to β or β to α
[37, 38]. In contrast, another class of GTs form glycosidic bonds in their products
having the same stereochemistry as their donor substrate [29].
Protein engineering of GTs is used to create a tool-box of enzymes with altered
substrate specificity or broader substrate promiscuity including unnatural glycan
structures [25, 39–42]. Further structural studies and directed evolution of GTs will
expand the large diversity of possible reactions.
Although Leloir-GTs are accepted as perfect candidates for the biocatalytic
production of glycans their dependence on nucleotide sugars makes cost effec-
tive synthesis strategies more complex. One approach to overcome this draw-
back is the (re)generation of donor-substrates with multienzyme systems [24,
43]. Especially, in situ regeneration schemes for nucleotide sugars are ideal
examples for enzymatic cascade reactions. More insight into these interest-
ing reactions and their possibilities are given in the subsequent parts of this
chapter.
In summary, GTs are outstanding for their regio- and stereospecificity as well as
their natural abundance. Many GTs have been expressed successfully. They show
close to quantitative conversion, use a broad range of acceptor substrates, and are
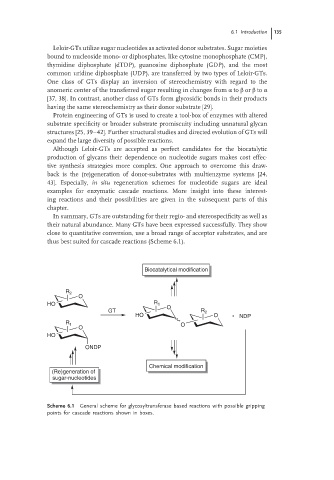
thus best suited for cascade reactions (Scheme 6.1).
Biocatalytical modification
R 2
O
HO R 1 O
GT R 2
HO O NDP
R 1 O
O
HO
ONDP
Chemical modification
(Re)generation of
sugar-nucleotides
Scheme 6.1 General scheme for glycosyltransferase based reactions with possible gripping
points for cascade reactions shown in boxes.