Page 165 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 165
6.2 Sequential Syntheses 141
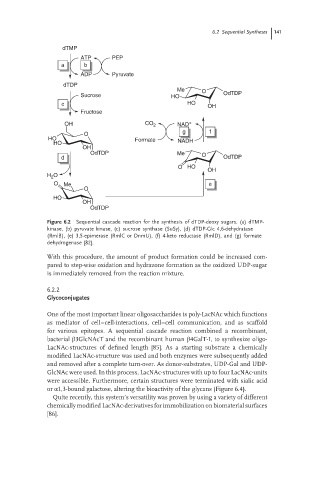
dTMP
ATP PEP
a b
ADP Pyruvate
dTDP
Me O
Sucrose HO OdTDP
c HO
OH
Fructose
OH CO 2 NAD +
g f
O
HO Formate NADH
HO
OH
OdTDP Me O
d OdTDP
O HO
OH
H O
2
O Me e
O
HO
OH
OdTDP
Figure 6.2 Sequential cascade reaction for the synthesis of dTDP-deoxy sugars. (a) dTMP-
kinase, (b) pyruvate kinase, (c) sucrose synthase (SuSy), (d) dTDP-Glc 4,6-dehydratase
(RmlB), (e) 3,5-epimerase (RmlC or DnmU), (f) 4-keto reductase (RmlD), and (g) formate
dehydrogenase [82].
With this procedure, the amount of product formation could be increased com-
pared to step-wise oxidation and hydrazone formation as the oxidized UDP-sugar
is immediately removed from the reaction mixture.
6.2.2
Glycoconjugates
One of the most important linear oligosaccharides is poly-LacNAc which functions
as mediator of cell–cell-interactions, cell–cell communication, and as scaffold
for various epitopes. A sequential cascade reaction combined a recombinant,
bacterial β3GlcNAcT and the recombinant human β4GalT-I, to synthesize oligo-
LacNAc-structures of defined length [85]. As a starting substrate a chemically
modified LacNAc-structure was used and both enzymes were subsequently added
and removed after a complete turn-over. As donor-substrates, UDP-Gal and UDP-
GlcNAc were used. In this process, LacNAc-structures with up to four LacNAc-units
were accessible. Furthermore, certain structures were terminated with sialic acid
or α1,3-bound galactose, altering the bioactivity of the glycans (Figure 6.4).
Quite recently, this system’s versatility was proven by using a variety of different
chemically modified LacNAc-derivatives for immobilization on biomaterial surfaces
[86].