Page 226 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 226
202 9 Stereoselective Hydrolase-Catalyzed Processes in Continuous-Flow Mode
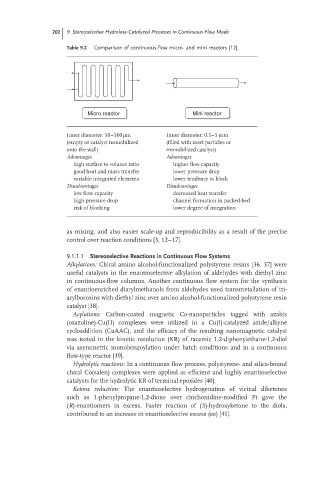
Table 9.2 Comparison of continuous-flow micro- and mini reactors [12].
Micro reactor Mini reactor
Inner diameter: 50–500 μm Inner diameter: 0.5–5 mm
(empty or catalyst immobilized (filled with inert particles or
onto the wall) immobilized catalyst)
Advantages Advantages
high surface to volume ratio higher flow capacity
good heat and mass transfer lower pressure drop
variable integrated elements lower tendency to block
Disadvantages Disadvantages
low flow capacity decreased heat transfer
high pressure drop channel formation in packed-bed
risk of blocking lower degree of integration
as mixing, and also easier scale-up and reproducibility as a result of the precise
control over reaction conditions [3, 12–17].
9.1.1.1 Stereoselective Reactions in Continuous Flow Systems
Alkylations: Chiral amino alcohol-functionalized polystyrene resins [36, 37] were
useful catalysts in the enantioselective alkylation of aldehydes with diethyl zinc
in continuous-flow columns. Another continuous flow system for the synthesis
of enantioenriched diarylmethanols from aldehydes used transmetallation of tri-
arylboroxins with diethyl zinc over amino alcohol-functionalized polystyrene resin
catalyst [38].
Acylations: Carbon-coated magnetic Co-nanoparticles tagged with azabis
(oxazoline)-Cu(II) complexes were utilized in a Cu(I)-catalyzed azide/alkyne
cycloaddition (CuAAC), and the efficacy of the resulting nanomagnetic catalyst
was tested in the kinetic resolution (KR) of racemic 1,2-diphenylethane-1,2-diol
via asymmetric monobenzoylation under batch conditions and in a continuous
flow-type reactor [39].
Hydrolytic reactions: In a continuous flow process, polystyrene- and silica-bound
chiral Co(salen) complexes were applied as efficient and highly enantioselective
catalysts for the hydrolytic KR of terminal epoxides [40].
Ketone reduction: The enantioselective hydrogenation of vicinal diketones
such as 1-phenylpropane-1,2-dione over cinchonidine-modified Pt gave the
(R)-enantiomers in excess. Faster reaction of (S)-hydroxyketone to the diols,
contributed to an increase in enantioselective excess (ee) [41].