Page 266 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 266
242 10 Perspectives on Multienzyme Process Technology
of the choices and decisions, which characterize process development of such
systems. Using the models, it becomes possible to focus experimental efforts and
develop the process faster than would otherwise have been the case.
For a multienzyme process, this evaluation is critically important to achieve a
better theoretical understanding of the process and to achieve useful modeling
and process design. The reaction considerations describe the key characteristics
to understand how the interaction between enzymes and components can be
interpreted for modeling. Furthermore, such information forms the basis for
the formulation of reaction rates for the different enzymes that are involved in
multienzyme process. In this manner, a preliminary idea of enzyme mechanisms
and kinetic parameters, that can be expected when developing a model, may be
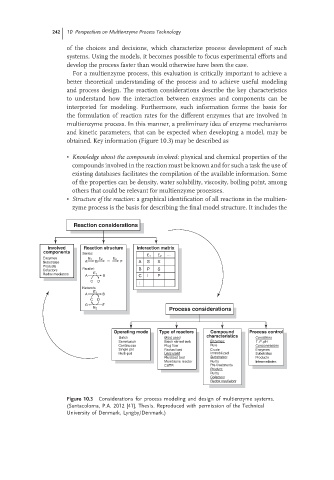
obtained. Key information (Figure 10.3) may be described as
• Knowledge about the compounds involved: physical and chemical properties of the
compounds involved in the reaction must be known and for such a task the use of
existing databases facilitates the compilation of the available information. Some
of the properties can be density, water solubility, viscosity, boiling point, among
others that could be relevant for multienzyme processes.
• Structure of the reaction: a graphical identification of all reactions in the multien-
zyme process is the basis for describing the final model structure. It includes the
Reaction considerations
Involved Reaction structure Interaction matrix
components Series:
E 1 E 2
Enzymes E 1 E 2 E n
Substrates A B P A S X
Products
Cofactors Parallel: B P S
Redox mediators A E 1 B C I P
C D
Network:
E 1
A B
C D
G F
E 2
Process considerations
Operating mode Type of reactors Compound Process control
characteristics
Batch Most used Conditions
Semi-batch Batch stirred tank Enzymes: T. P. pH
Continuous Plug flow Pure Concentrations
Single pot Packed bed Crude Enzymes
Multi-pot Less used Immobilized Substrates
Fluidized bed Substrates: Products
Membrane reactor Purity Intermediates
CSTR Pre-treatments
Product:
Purity
Cofactors
Redox mediators
Figure 10.3 Considerations for process modeling and design of multienzyme systems.
(Santacoloma, P.A. 2012 [41], Thesis. Reproduced with permission of the Technical
University of Denmark, Lyngby/Denmark.)