Page 107 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 107
4.4 Mathematical Modeling of the Synthesis of Aliphatic Polyesters 85
100
80
Total mass loss (%) 60
40
PPSeb
PPSeb/MWCNTs
20
PPSEb/SiO 2
PPSeb/MMT
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Days
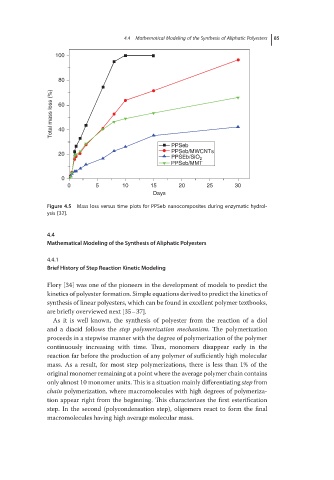
Figure 4.5 Mass loss versus time plots for PPSeb nanocomposites during enzymatic hydrol-
ysis [32].
4.4
Mathematical Modeling of the Synthesis of Aliphatic Polyesters
4.4.1
Brief History of Step Reaction Kinetic Modeling
Flory [34] was one of the pioneers in the development of models to predict the
kinetics of polyester formation. Simple equations derived to predict the kinetics of
synthesis of linear polyesters, which can be found in excellent polymer textbooks,
are briefly overviewed next [35–37].
As it is well known, the synthesis of polyester from the reaction of a diol
and a diacid follows the step polymerization mechanism. The polymerization
proceeds in a stepwise manner with the degree of polymerization of the polymer
continuously increasing with time. Thus, monomers disappear early in the
reaction far before the production of any polymer of sufficiently high molecular
mass. As a result, for most step polymerizations, there is less than 1% of the
original monomer remaining at a point where the average polymer chain contains
only almost 10 monomer units. This is a situation mainly differentiating step from
chain polymerization, where macromolecules with high degrees of polymeriza-
tion appear right from the beginning. This characterizes the first esterification
step. In the second (polycondensation step), oligomers react to form the final
macromolecules having high average molecular mass.