Page 105 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 105
4.3 Properties of Poly(propylene alkylenedicarboxylates) 83
attributed to its chemical structure, and especially to its flexible butylene units. On
the other hand, retardation in PPSu crystallization is due to its reduced symmetry
caused by the propylene units.
The melting point and degree of crystallinity of a polyester can also affect its
biodegradability. This is very important as all the known aliphatic polyesters
degrade in a short time when they are adapted to the environment. The enzymatic
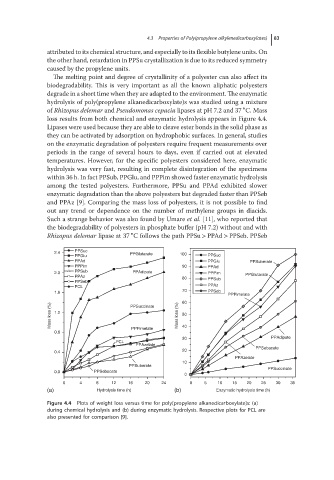
hydrolysis of poly(propylene alkanedicarboxylate)s was studied using a mixture
∘
of Rhizopus delemar and Pseudomonas cepacia lipases at pH 7.2 and 37 C. Mass
loss results from both chemical and enzymatic hydrolysis appears in Figure 4.4.
Lipases were used because they are able to cleave ester bonds in the solid phase as
they can be activated by adsorption on hydrophobic surfaces. In general, studies
on the enzymatic degradation of polyesters require frequent measurements over
periods in the range of several hours to days, even if carried out at elevated
temperatures. However, for the specific polyesters considered here, enzymatic
hydrolysis was very fast, resulting in complete disintegration of the specimens
within 36 h. In fact PPSub, PPGlu, and PPPim showed faster enzymatic hydrolysis
among the tested polyesters. Furthermore, PPSu and PPAd exhibited slower
enzymatic degradation than the above polyesters but degraded faster than PPSeb
and PPAz [9]. Comparing the mass loss of polyesters, it is not possible to find
out any trend or dependence on the number of methylene groups in diacids.
Such a strange behavior was also found by Umare et al. [11], who reported that
the biodegradability of polyesters in phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) without and with
∘
Rhizopus delemar lipase at 37 Cfollows thepathPPSu > PPAd > PPSeb. PPSeb
2.4 PPSuc PPGlutarate 100
PPGlu PPSuc
PPAd PPGlu PPSuberate
PPPim 90 PPAd
2.0 PPSub PPAdipate PPPim
PPAz 80 PPSub PPGlutarate
PPSeb
PCL PPAz
1.6 70 PPSeb
PPPimelate
60
Mass loss (%) 1.2 PPSuccinate Mass loss (%) 50
0.8 PPPimelate 40
30 PPAdipate
PCL
PPAzelate
PPSebacate
0.4 20
PPAzelate
10
PPSuberate
PPSuccinate
0.0 PPSebacate
0
0 4 8 12 16 20 24 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35
(a) Hydrolysis time (h) (b) Enzymatic hydrolysis time (h)
Figure 4.4 Plots of weight loss versus time for poly(propylene alkanedicarboxylate)s: (a)
during chemical hydrolysis and (b) during enzymatic hydrolysis. Respective plots for PCL are
also presented for comparison [9].