Page 101 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 101
4.2 Synthesis of Aliphatic Polyesters from 1,3-Propanediol and Aliphatic Acids 79
is further reduced. For this reason, some polyfunctional comonomers are added
in low amounts (0.5–1 wt%) together with aliphatic acids and diols in order to
®
prepare branched macromolecules, as in the case of Bionolle .
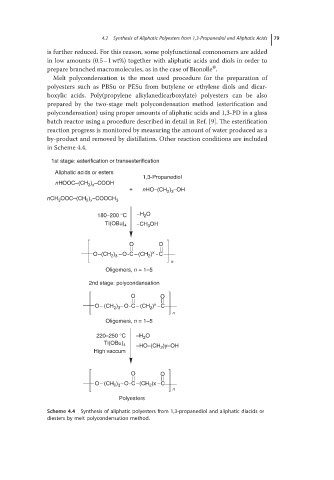
Melt polycondensation is the most used procedure for the preparation of
polyesters such as PBSu or PESu from butylene or ethylene diols and dicar-
boxylic acids. Poly(propylene alkylanedicarboxylate) polyesters can be also
prepared by the two-stage melt polycondensation method (esterification and
polycondensation) using proper amounts of aliphatic acids and 1,3-PD in a glass
batch reactor using a procedure described in detail in Ref. [9]. The esterification
reaction progress is monitored by measuring the amount of water produced as a
by-product and removed by distillation. Other reaction conditions are included
in Scheme 4.4.
1st stage: esterification or transesterification
Aliphatic acids or esters
1,3-Propanediol
nHOOC–(CH 2 ) x –COOH
+ nHO–(CH 2 ) 3 –OH
OOC–(CH ) –COOCH
nCH 3 2 x 3
180–200 °C −H O
2
−CH 3 OH
Ti(OBu) 4
O O
OC (CH 2 ) x C
O (CH 2 ) 3
n
Oligomers, n = 1–5
2nd stage: polycondansation
O O
O (CH ) OC (CH 2 ) x C
2 3
n
Oligomers, n = 1–5
220–250 °C –H 2 O
–HO–(CH 2 )y–OH
Ti(OBu) 4
High vaccum
O O
OC (CH 2 )x C
O (CH 2 ) 3
n
Polyesters
Scheme 4.4 Synthesis of aliphatic polyesters from 1,3-propanediol and aliphatic diacids or
diesters by melt polycondensation method.