Page 100 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 100
78 4 Synthesis, Properties, and Mathematical Modeling of Biodegradable Aliphatic Polyesters
Biodiesel Feedstocks Hemicellulosic
wastes wastes
Glycerol 0,5 Glucose 0,6 Xylose
3-HPA
H O
6 12
5 10
C 3 8 3 C H O 6 C H O 5
2 NAD + NAD + NAD +
2 NADH 2 NADH 2
NADH 2
GAP DHAP
Pyruvate
+
NADH 2
succinate
Byproducts
1,3-PDO 1,4-BDO 1,2-PDO 2,3-BDO
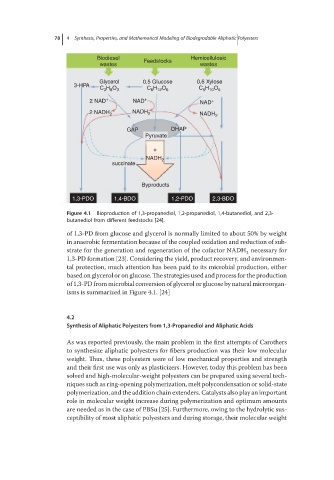
Figure 4.1 Bioproduction of 1,3-propanediol, 1,2-propanediol, 1,4-butanediol, and 2,3-
butanediol from different feedstocks [24].
of 1,3-PD from glucose and glycerol is normally limited to about 50% by weight
in anaerobic fermentation because of the coupled oxidation and reduction of sub-
strate for the generation and regeneration of the cofactor NADH necessary for
2
1,3-PD formation [23]. Considering the yield, product recovery, and environmen-
tal protection, much attention has been paid to its microbial production, either
based on glycerol or on glucose. The strategies used and process for the production
of 1,3-PD from microbial conversion of glycerol or glucose by natural microorgan-
isms is summarized in Figure 4.1. [24]
4.2
Synthesis of Aliphatic Polyesters from 1,3-Propanediol and Aliphatic Acids
As was reported previously, the main problem in the first attempts of Carothers
to synthesize aliphatic polyesters for fibers production was their low molecular
weight. Thus, these polyesters were of low mechanical properties and strength
and their first use was only as plasticizers. However, today this problem has been
solved and high-molecular-weight polyesters can be prepared using several tech-
niques such as ring-opening polymerization, melt polycondensation or solid-state
polymerization, and the addition chain extenders. Catalysts also play an important
role in molecular weight increase during polymerization and optimum amounts
are needed as in the case of PBSu [25]. Furthermore, owing to the hydrolytic sus-
ceptibility of most aliphatic polyesters and during storage, their molecular weight