Page 144 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 144
122 5 Crystallization of Poly(lactic acid)
More importantly, the crystallization kinetics of all samples of different molar
mass displays the characteristic discontinuity due to the different radial growth
′
rates of α -and α-spherulites. Independent of the molar mass, the transition from
∘
′
growth of α -crystals to growth of α-crystals occurs at 100–120 C [28].
5.5
Influence of Comonomer Content
As mentioned above, PLA should be addressed as a random copolymer rather
than as a homopolymer; the properties of the former depend on the ratio between
L-lactic acid and D-lactic acid units. A few studies describe the influence of the
concentration of D-lactic acid co-units in the PLLA macromolecule on the crys-
tallization kinetics [15, 37, 77–79]. The incorporation of D-lactic acid co-units
reduces the radial growth rate of spherulites and increases the induction period
of spherulite formation, as is typical for random copolymers. In a recent work, the
influence of the chain structure on the crystal polymorphism of PLA was detailed
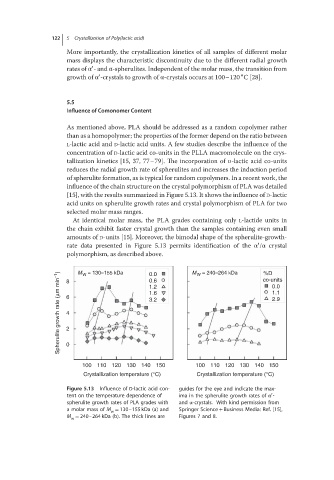
[15], with the results summarized in Figure 5.13. It shows the influence of D-lactic
acid units on spherulite growth rates and crystal polymorphism of PLA for two
selected molar mass ranges.
At identical molar mass, the PLA grades containing only L-lactide units in
the chain exhibit faster crystal growth than the samples containing even small
amounts of D-units [15]. Moreover, the bimodal shape of the spherulite-growth-
′
rate data presented in Figure 5.13 permits identification of the α /α crystal
polymorphism, as described above. M W = 240–264 kDa co-units
M W = 130–155 kDa
%D
Spherulite growth rate (μm min –1 ) 6 4 2 1.2 0.0
0.0
0.6
8
1.1
1.6
2.9
3.2
0
100 110 120 130 140 150 100 110 120 130 140 150
Crystallization temperature (°C) Crystallization temperature (°C)
Figure 5.13 Influence of D-lactic acid con- guides for the eye and indicate the max-
′
tent on the temperature dependence of ima in the spherulite growth rates of α -
spherulite growth rates of PLA grades with and α-crystals. With kind permission from
a molar mass of M = 130–155 kDa (a) and Springer Science + Business Media: Ref. [15],
w
M = 240–264 kDa (b). The thick lines are Figures 7 and 8.
w