Page 277 - Biofuels Refining and Performance
P. 277
256 Chapter Nine
Electric current
− −
e e
t
Depleted fuel e − Electric curren − Water
e
Hydrogen molecule
H + Oxygen molecule
H O Water
2
H 2
+
Hydrogen ion (H )
O 2
H +
H 2 Air in
Anode Cathode
Electrolyte Gas diffusion layer
Gas diffusion layer
(PEM) Cathode
Anode
catalyst layer
catalyst layer
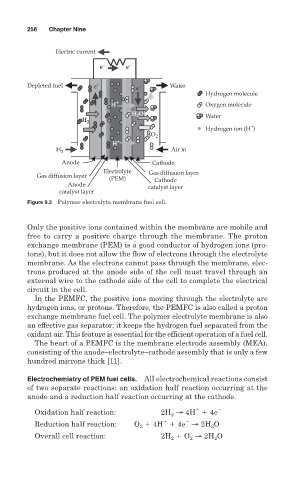
Figure 9.3 Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell.
Only the positive ions contained within the membrane are mobile and
free to carry a positive charge through the membrane. The proton
exchange membrane (PEM) is a good conductor of hydrogen ions (pro-
tons), but it does not allow the flow of electrons through the electrolyte
membrane. As the electrons cannot pass through the membrane, elec-
trons produced at the anode side of the cell must travel through an
external wire to the cathode side of the cell to complete the electrical
circuit in the cell.
In the PEMFC, the positive ions moving through the electrolyte are
hydrogen ions, or protons. Therefore, the PEMFC is also called a proton
exchange membrane fuel cell. The polymer electrolyte membrane is also
an effective gas separator; it keeps the hydrogen fuel separated from the
oxidant air. This feature is essential for the efficient operation of a fuel cell.
The heart of a PEMFC is the membrane electrode assembly (MEA),
consisting of the anode–electrolyte–cathode assembly that is only a few
hundred microns thick [11].
Electrochemistry of PEM fuel cells. All electrochemical reactions consist
of two separate reactions: an oxidation half reaction occurring at the
anode and a reduction half reaction occurring at the cathode.
Oxidation half reaction: 2H 2 → 4H 4e
Reduction half reaction: O 4H 4e → 2H O
2
2
Overall cell reaction: 2H O → 2H O
2
2
2