Page 173 - Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis And Torrefaction Practical Design and Theory
P. 173
150 Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction
Radiative and Gas
convective
heat
Thermal
boundary Liquid
layer
Biomass Tar Char
Conduction
and pore
convection Gas
Char
Primary decomposition Gas phase secondary
reactions tar cracking reactions
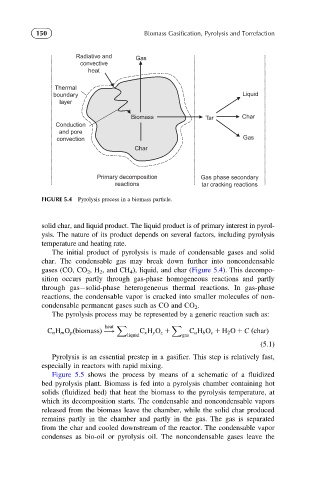
FIGURE 5.4 Pyrolysis process in a biomass particle.
solid char, and liquid product. The liquid product is of primary interest in pyrol-
ysis. The nature of its product depends on several factors, including pyrolysis
temperature and heating rate.
The initial product of pyrolysis is made of condensable gases and solid
char. The condensable gas may break down further into noncondensable
gases (CO, CO 2 ,H 2 , and CH 4 ), liquid, and char (Figure 5.4). This decompo-
sition occurs partly through gas-phase homogeneous reactions and partly
through gas solid-phase heterogeneous thermal reactions. In gas-phase
reactions, the condensable vapor is cracked into smaller molecules of non-
condensable permanent gases such as CO and CO 2 .
The pyrolysis process may be represented by a generic reaction such as:
heat X X
C n H m O p ðbiomassÞ ! C x H y O z 1 C a H b O c 1 H 2 O 1 C ðcharÞ
liquid gas
(5.1)
Pyrolysis is an essential prestep in a gasifier. This step is relatively fast,
especially in reactors with rapid mixing.
Figure 5.5 shows the process by means of a schematic of a fluidized
bed pyrolysis plant. Biomass is fed into a pyrolysis chamber containing hot
solids (fluidized bed) that heat the biomass to the pyrolysis temperature, at
which its decomposition starts. The condensable and noncondensable vapors
released from the biomass leave the chamber, while the solid char produced
remains partly in the chamber and partly in the gas. The gas is separated
from the char and cooled downstream of the reactor. The condensable vapor
condenses as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil. The noncondensable gases leave the