Page 83 - Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis And Torrefaction Practical Design and Theory
P. 83
Chapter | 3 Biomass Characteristics 61
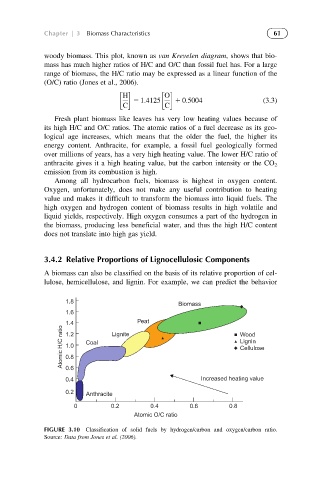
woody biomass. This plot, known as van Krevelen diagram, shows that bio-
mass has much higher ratios of H/C and O/C than fossil fuel has. For a large
range of biomass, the H/C ratio may be expressed as a linear function of the
(O/C) ratio (Jones et al., 2006).
H O
5 1:4125 1 0:5004 (3.3)
C C
Fresh plant biomass like leaves has very low heating values because of
its high H/C and O/C ratios. The atomic ratios of a fuel decrease as its geo-
logical age increases, which means that the older the fuel, the higher its
energy content. Anthracite, for example, a fossil fuel geologically formed
over millions of years, has a very high heating value. The lower H/C ratio of
anthracite gives it a high heating value, but the carbon intensity or the CO 2
emission from its combustion is high.
Among all hydrocarbon fuels, biomass is highest in oxygen content.
Oxygen, unfortunately, does not make any useful contribution to heating
value and makes it difficult to transform the biomass into liquid fuels. The
high oxygen and hydrogen content of biomass results in high volatile and
liquid yields, respectively. High oxygen consumes a part of the hydrogen in
the biomass, producing less beneficial water, and thus the high H/C content
does not translate into high gas yield.
3.4.2 Relative Proportions of Lignocellulosic Components
A biomass can also be classified on the basis of its relative proportion of cel-
lulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. For example, we can predict the behavior
1.8 Biomass
1.6 Peat
Atomic H/C ratio 1.4 Coal Lignite Wood
1.2
Lignin
1.0
Cellulose
0.8
0.6
0.4 Increased heating value
0.2 Anthracite
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
Atomic O/C ratio
FIGURE 3.10 Classification of solid fuels by hydrogen/carbon and oxygen/carbon ratio.
Source: Data from Jones et al. (2006).