Page 169 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 1, Fundamentals
P. 169
146 BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN BODY
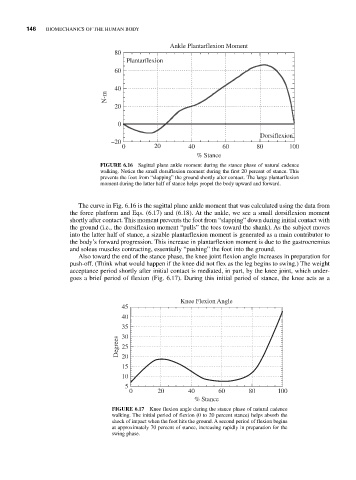
Ankle Plantarflexion Moment
80
Plantarflexion
60
40
N-m
20
0
Dorsiflexion
–20
0 20 40 60 80 100
% Stance
FIGURE 6.16 Sagittal plane ankle moment during the stance phase of natural cadence
walking. Notice the small dorsiflexion moment during the first 20 percent of stance. This
prevents the foot from “slapping” the ground shortly after contact. The large plantarflexion
moment during the latter half of stance helps propel the body upward and forward.
The curve in Fig. 6.16 is the sagittal plane ankle moment that was calculated using the data from
the force platform and Eqs. (6.17) and (6.18). At the ankle, we see a small dorsiflexion moment
shortly after contact. This moment prevents the foot from “slapping” down during initial contact with
the ground (i.e., the dorsiflexion moment “pulls” the toes toward the shank). As the subject moves
into the latter half of stance, a sizable plantarflexion moment is generated as a main contributor to
the body’s forward progression. This increase in plantarflexion moment is due to the gastrocnemius
and soleus muscles contracting, essentially “pushing” the foot into the ground.
Also toward the end of the stance phase, the knee joint flexion angle increases in preparation for
push-off. (Think what would happen if the knee did not flex as the leg begins to swing.) The weight
acceptance period shortly after initial contact is mediated, in part, by the knee joint, which under-
goes a brief period of flexion (Fig. 6.17). During this initial period of stance, the knee acts as a
Knee Flexion Angle
45
40
35
Degrees 30
25
20
15
10
5
0 20 40 60 80 100
% Stance
FIGURE 6.17 Knee flexion angle during the stance phase of natural cadence
walking. The initial period of flexion (0 to 20 percent stance) helps absorb the
shock of impact when the foot hits the ground. A second period of flexion begins
at approximately 70 percent of stance, increasing rapidly in preparation for the
swing phase.