Page 28 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 1, Fundamentals
P. 28
MODELING OF BIOMEDICAL SYSTEMS 5
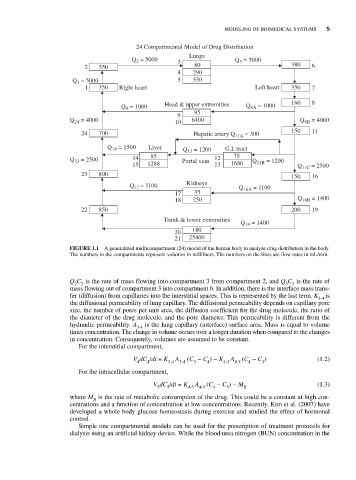
24 Compartmental Model of Drug Distribution
Lungs
Q 2 = 5000 Q 3 = 5000
3
2 350 80 380 6
4 290
Q 1 = 5000 5 550
1 350 Right heart Left heart 350 7
Q 9 = 1000 Head & upper extremities Q 8A = 1000 160 8
95
9
Q 24 = 4000 10 6400 Q 8B = 4000
150 11
24 700 Hepatic artery Q 11A = 300
Q 14 = 1500 Liver Q 12 = 1200 G.I. tract
Q 23 = 2500 14 85 Portal vein 12 75 Q 11B = 1200
15 1288 13 1680 Q 11C = 2500
23 800 150 16
Kidneys
Q 17 = 1100 Q 16A = 1100
17 35
18 250 Q 16B = 1400
22 850 200 19
Trunk & lower extremities
Q 19 = 1400
20 180
21 25400
FIGURE 1.1 A generalized multicompartment (24) model of the human body to analyze drug distribution in the body.
The numbers in the compartments represent volumes in milliliters. The numbers on the lines are flow rates in mL/min.
Q C is the rate of mass flowing into compartment 3 from compartment 2, and Q C is the rate of
2 2 3 3
mass flowing out of compartment 3 into compartment 6. In addition, there is the interface mass trans-
fer (diffusion) from capillaries into the interstitial spaces. This is represented by the last term. K is
3-4
the diffusional permeability of lung capillary. The diffusional permeability depends on capillary pore
size, the number of pores per unit area, the diffusion coefficient for the drug molecule, the ratio of
the diameter of the drug molecule, and the pore diameter. This permeability is different from the
hydraulic permeability. A is the lung capillary (interface) surface area. Mass is equal to volume
3-4
times concentration. The change in volume occurs over a longer duration when compared to the changes
in concentration. Consequently, volumes are assumed to be constant.
For the interstitial compartment,
V dC /dt = K A (C − C ) − K A (C − C ) (1.2)
4 4 3-4 3-4 3 4 4-5 4-5 4 5
For the intracellular compartment,
V dC /dt = K A (C − C ) − M (1.3)
5 5 4-5 4-5 4 5 R
where M is the rate of metabolic consumption of the drug. This could be a constant at high con-
R
centrations and a function of concentration at low concentrations. Recently, Kim et al. (2007) have
developed a whole body glucose homeostasis during exercise and studied the effect of hormonal
control.
Simple one compartmental models can be used for the prescription of treatment protocols for
dialysis using an artificial kidney device. While the blood urea nitrogen (BUN) concentration in the