Page 33 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 1, Fundamentals
P. 33
10 BIOMEDICAL SYSTEMS ANALYSIS
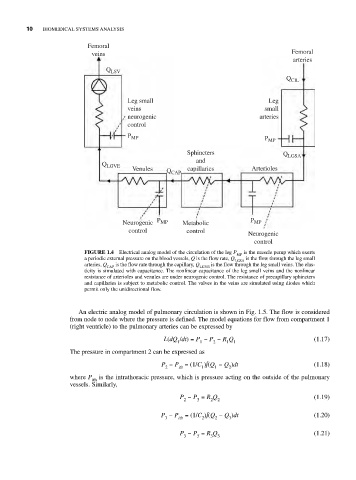
Femoral
veins Femoral
arteries
Q LSV
Q CIL
Leg small Leg
veins small
neurogenic arteries
control
P MP P MP
Sphincters Q LGSA
and
Q LGVE
Venules Q CAP capillaries Arterioles
P P
Neurogenic MP Metabolic MP
control control Neurogenic
control
FIGURE 1.4 Electrical analog model of the circulation of the leg P is the muscle pump which exerts
MP
a periodic external pressure on the blood vessels, Q is the flow rate, Q is the flow through the leg small
LGSA
arteries, Q is the flow rate through the capillary, Q is the flow through the leg small veins. The elas-
CAP LGVE
ticity is simulated with capacitance. The nonlinear capacitance of the leg small veins and the nonlinear
resistance of arterioles and venules are under neurogenic control. The resistance of precapillary sphincters
and capillaries is subject to metabolic control. The valves in the veins are simulated using diodes which
permit only the unidirectional flow.
An electric analog model of pulmonary circulation is shown in Fig. 1.5. The flow is considered
from node to node where the pressure is defined. The model equations for flow from compartment 1
(right ventricle) to the pulmonary arteries can be expressed by
L(dQ /dt) = P − P − R Q (1.17)
1 1 2 1 1
The pressure in compartment 2 can be expressed as
P − P = (1/C )∫(Q − Q )dt (1.18)
2 ith 1 1 2
where P is the intrathoracic pressure, which is pressure acting on the outside of the pulmonary
ith
vessels. Similarly,
P − P = R Q (1.19)
2 3 2 2
P − P = (1/C )∫(Q − Q )dt (1.20)
3 ith 2 2 3
P − P = R Q (1.21)
3 5 3 3