Page 354 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 1, Fundamentals
P. 354
BIOPOLYMERS 331
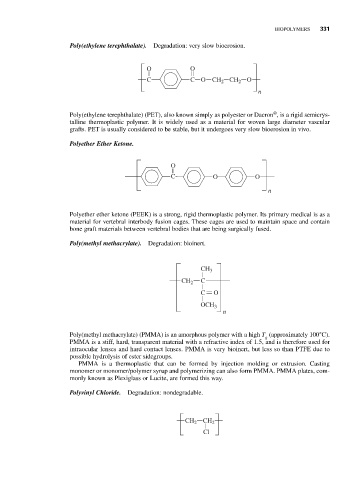
Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Degradation: very slow bioerosion.
O O
C CO CH 2 CH 2 O
n
®
Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET), also known simply as polyester or Dacron , is a rigid semicrys-
talline thermoplastic polymer. It is widely used as a material for woven large diameter vascular
grafts. PET is usually considered to be stable, but it undergoes very slow bioerosion in vivo.
Polyether Ether Ketone.
O
C O O
n
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a strong, rigid thermoplastic polymer. Its primary medical is as a
material for vertebral interbody fusion cages. These cages are used to maintain space and contain
bone graft materials between vertebral bodies that are being surgically fused.
Poly(methyl methacrylate). Degradation: bioinert.
CH 3
CH 2 C
C O
OCH 3
n
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) is an amorphous polymer with a high T (approximately 100°C).
g
PMMA is a stiff, hard, transparent material with a refractive index of 1.5, and is therefore used for
intraocular lenses and hard contact lenses. PMMA is very bioinert, but less so than PTFE due to
possible hydrolysis of ester sidegroups.
PMMA is a thermoplastic that can be formed by injection molding or extrusion. Casting
monomer or monomer/polymer syrup and polymerizing can also form PMMA. PMMA plates, com-
monly known as Plexiglass or Lucite, are formed this way.
Polyvinyl Chloride. Degradation: nondegradable.
CH 2 CH 2
Cl