Page 167 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 2, Applications
P. 167
146 MEDICAL DEVICE DESIGN
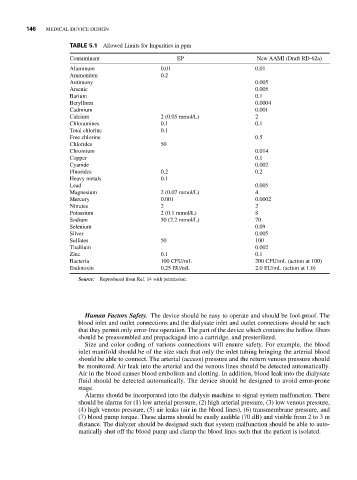
TABLE 5.1 Allowed Limits for Impurities in ppm
Contaminant EP New AAMI (Draft RD-62a)
Aluminum 0.01 0.01
Ammonium 0.2
Antimony 0.005
Arsenic 0.005
Barium 0.1
Beryllium 0.0004
Cadmium 0.001
Calcium 2 (0.05 mmol/L) 2
Chloramines 0.1 0.1
Total chlorine 0.1
Free chlorine 0.5
Chlorides 50
Chromium 0.014
Copper 0.1
Cyanide 0.002
Fluorides 0.2 0.2
Heavy metals 0.1
Lead 0.005
Magnesium 2 (0.07 mmol/L) 4
Mercury 0.001 0.0002
Nitrates 2 2
Potassium 2 (0.1 mmol/L) 8
Sodium 50 (2.2 mmol/L) 70
Selenium 0.09
Silver 0.005
Sulfates 50 100
Thallium 0.002
Zinc 0.1 0.1
Bacteria 100 CFU/mL 200 CFU/mL (action at 100)
Endotoxin 0.25 EU/mL 2.0 EU/mL (action at 1.0)
Source: Reproduced from Ref. 14 with permission.
Human Factors Safety. The device should be easy to operate and should be fool-proof. The
blood inlet and outlet connections and the dialysate inlet and outlet connections should be such
that they permit only error-free operation. The part of the device which contains the hollow fibers
should be preassembled and prepackaged into a cartridge, and presterilized.
Size and color coding of various connections will ensure safety. For example, the blood
inlet manifold should be of the size such that only the inlet tubing bringing the arterial blood
should be able to connect. The arterial (access) pressure and the return venous pressure should
be monitored. Air leak into the arterial and the venous lines should be detected automatically.
Air in the blood causes blood embolism and clotting. In addition, blood leak into the dialysate
fluid should be detected automatically. The device should be designed to avoid error-prone
stage.
Alarms should be incorporated into the dialysis machine to signal system malfunction. There
should be alarms for (1) low arterial pressure, (2) high arterial pressure, (3) low venous pressure,
(4) high venous pressure, (5) air leaks (air in the blood lines), (6) transmembrane pressure, and
(7) blood pump torque. These alarms should be easily audible (70 dB) and visible from 2 to 3 m
distance. The dialyzer should be designed such that system malfunction should be able to auto-
matically shut off the blood pump and clamp the blood lines such that the patient is isolated.