Page 114 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 114
Soil and W ater Conservation 95
of the soil–water/air interface. Percolation occurs in a vertical direc-
tion, and it only takes place in the zone above the water table.
Runoff This is the part of precipitation, snow melt, or irrigation water
flowing on the earth’s surface in creeks, streams, rivers, drainage
ditches, sewers, and the like. Runoff could be generated as a result of
excess water not infiltrating the soil or by exfiltration of the soil water.
Groundwater This is the water stored in the soil pore spaces and frac-
tures of geologic formations that are saturated with water. The top
of the water surface in unconfined aquifers is called the water table. It
is the surface where water pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure.
Water can move in all directions in the groundwater zone.
Groundwater Recharge Water percolating deep into the soil will even-
tually feed into the groundwater. This process of water replenishing
the groundwater is called groundwater recharge. Conversely, if the
groundwater feeds a river or a spring, then it is called discharge.
Snow Melt When snow melts, it either becomes surface runoff or
infiltrates the soil. If the soil beneath the snow is frozen, then all the
snow melt becomes runoff. Sometimes snow can evaporate directly
without turning into liquid. This process of phase change directly
from solid into gaseous form is called sublimation.
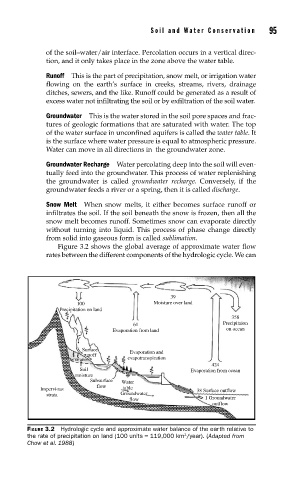
Figure 3.2 shows the global average of approximate water flow
rates between the different components of the hydrologic cycle. We can
39
100 Moisture over land
Precipitation on land
358
61 Precipitaion
Evaporation from land on ocean
Surface
runoff Evaporation and
Infitiration evapotranspiration
424
Soil Evaporation from ocean
moisture
Subsurface Water
flow
Impervious table 38 Surface outflow
strata Groundwater
flow 1 Groundwater
outflow
FIGURE 3.2 Hydrologic cycle and approximate water balance of the earth relative to
the rate of precipitation on land (100 units = 119,000 km /year). (Adapted from
3
Chow et al. 1988)