Page 26 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 26
Micr oarray Data Analysis Using Machine Learning Methods 7
1.2.2 Support Vector Machines
Support vector machines are suitable for classification problems that
involve high dimensionality. They are learning kernel-based systems
that use a hypothesis space of linear functions in high-dimensional
feature spaces. Unlike artificial neural networks, which try to define
complex functions in the input feature space, kernel methods per-
form a nonlinear mapping of complex data into high-dimensional
feature spaces and then use simple linear functions to create linear
decision boundaries. Thus, the problem of choosing network archi-
tecture is replaced here by the problem of choosing a suitable kernel
for data projection.
The advantages of support vector machines over neural networks
is that they are significantly faster to train, better suited to work with
high-dimensional data, provide better generalization ability on an
independent dataset, can be developed with few training examples,
and allow for scaling the importance of outliers. SVM parameters are
determined based on structural risk minimization. For example, in a
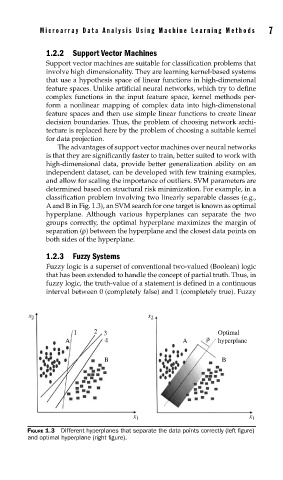
classification problem involving two linearly separable classes (e.g.,
A and B in Fig. 1.3), an SVM search for one target is known as optimal
hyperplane. Although various hyperplanes can separate the two
groups correctly, the optimal hyperplane maximizes the margin of
separation (ρ) between the hyperplane and the closest data points on
both sides of the hyperplane.
1.2.3 Fuzzy Systems
Fuzzy logic is a superset of conventional two-valued (Boolean) logic
that has been extended to handle the concept of partial truth. Thus, in
fuzzy logic, the truth-value of a statement is defined in a continuous
interval between 0 (completely false) and 1 (completely true). Fuzzy
x 2 x 2
1 2 3 Optimal
A 4 A ρ hyperplane
B B
x 1 x 1
FIGURE 1.3 Different hyperplanes that separate the data points correctly (left fi gure)
and optimal hyperplane (right fi gure).