Page 27 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 27
8 Cha pte r O n e
1
Membership 0.5 Low Med High
0 0.5 1
Expression level
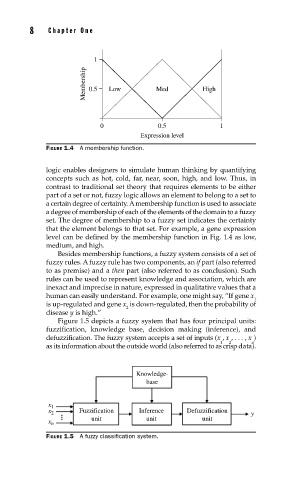
FIGURE 1.4 A membership function.
logic enables designers to simulate human thinking by quantifying
concepts such as hot, cold, far, near, soon, high, and low. Thus, in
contrast to traditional set theory that requires elements to be either
part of a set or not, fuzzy logic allows an element to belong to a set to
a certain degree of certainty. A membership function is used to associate
a degree of membership of each of the elements of the domain to a fuzzy
set. The degree of membership to a fuzzy set indicates the certainty
that the element belongs to that set. For example, a gene expression
level can be defined by the membership function in Fig. 1.4 as low,
medium, and high.
Besides membership functions, a fuzzy system consists of a set of
fuzzy rules. A fuzzy rule has two components, an if part (also referred
to as premise) and a then part (also referred to as conclusion). Such
rules can be used to represent knowledge and association, which are
inexact and imprecise in nature, expressed in qualitative values that a
human can easily understand. For example, one might say, “If gene x
1
is up-regulated and gene x is down-regulated, then the probability of
2
disease y is high.”
Figure 1.5 depicts a fuzzy system that has four principal units:
fuzzification, knowledge base, decision making (inference), and
defuzzification. The fuzzy system accepts a set of inputs (x , x , . . . , x )
1 2 n
as its information about the outside world (also referred to as crisp data).
Knowledge-
base
x 1
x 2 Fuzzification Inference Defuzzification y
unit unit unit
x n
FIGURE 1.5 A fuzzy classifi cation system.