Page 353 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 353
330 Cha pte r Ele v e n
Blow Molding The blow molding process involves blowing into a
molten thermoplastic tube with high-pressure air to conform to the
shape of a cooled mold. Air or nitrogen gas is introduced into the
tube causing the molten mass to expand against the walls of the mold
where it solidifies on cooling. The mold is then opened to remove the
container. There are three common types of blow molding: extrusion
blow molding, injection blow molding, and injection stretch blow
molding. 1,2,6
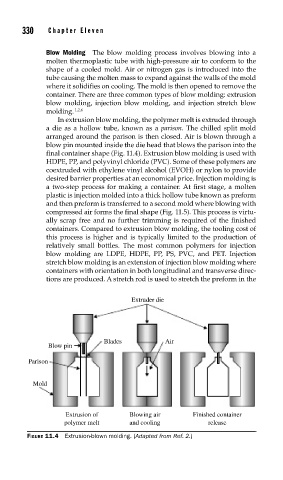
In extrusion blow molding, the polymer melt is extruded through
a die as a hollow tube, known as a parison. The chilled split mold
arranged around the parison is then closed. Air is blown through a
blow pin mounted inside the die head that blows the parison into the
final container shape (Fig. 11.4). Extrusion blow molding is used with
HDPE, PP, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Some of these polymers are
coextruded with ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH) or nylon to provide
desired barrier properties at an economical price. Injection molding is
a two-step process for making a container. At first stage, a molten
plastic is injection molded into a thick hollow tube known as preform
and then preform is transferred to a second mold where blowing with
compressed air forms the final shape (Fig. 11.5). This process is virtu-
ally scrap free and no further trimming is required of the finished
containers. Compared to extrusion blow molding, the tooling cost of
this process is higher and is typically limited to the production of
relatively small bottles. The most common polymers for injection
blow molding are LDPE, HDPE, PP, PS, PVC, and PET. Injection
stretch blow molding is an extension of injection blow molding where
containers with orientation in both longitudinal and transverse direc-
tions are produced. A stretch rod is used to stretch the preform in the
Extruder die
Blades Air
Blow pin
Parison
Mold
Extrusion of Blowing air Finished container
polymer melt and cooling release
FIGURE 11.4 Extrusion-blown molding. (Adapted from Ref. 2.)