Page 259 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 259
244 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
once again enters the compressor and the cycle
continues.
The effectiveness of all mechanically driv-
en vapor compression heat pumps is specified in
terms of coefficient of performance (COP) defined
as:
Useful thermal energy output
COP = ———————————————
Work input to the compressor
A COP of 5 means using one unit of work
input (in the form of electrical energy to power
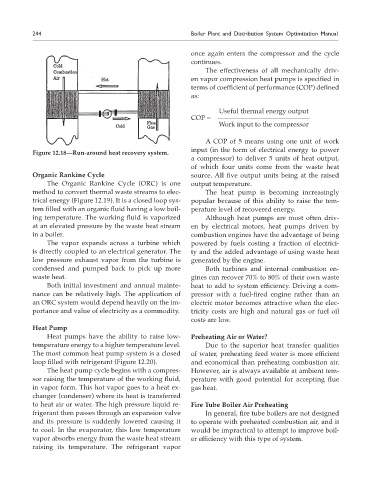
Figure 12.18—Run-around heat recovery system.
a compressor) to deliver 5 units of heat output,
of which four units come from the waste heat
Organic Rankine Cycle source. All five output units being at the raised
The Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) is one output temperature.
method to convert thermal waste streams to elec- The heat pump is becoming increasingly
trical energy (Figure 12.19). It is a closed loop sys- popular because of this ability to raise the tem-
tem filled with an organic fluid having a low boil- perature level of recovered energy.
ing temperature. The working fluid is vaporized Although heat pumps are most often driv-
at an elevated pressure by the waste heat stream en by electrical motors, heat pumps driven by
in a boiler. combustion engines have the advantage of being
The vapor expands across a turbine which powered by fuels costing a fraction of electrici-
is directly coupled to an electrical generator. The ty and the added advantage of using waste heat
low pressure exhaust vapor from the turbine is generated by the engine.
condensed and pumped back to pick up more Both turbines and internal combustion en-
waste heat. gines can recover 70% to 80% of their own waste
Both initial investment and annual mainte- heat to add to system efficiency. Driving a com-
nance can be relatively high. The application of pressor with a fuel-fired engine rather than an
an ORC system would depend heavily on the im- electric motor becomes attractive when the elec-
portance and value of electricity as a commodity. tricity costs are high and natural gas or fuel oil
costs are low.
Heat Pump
Heat pumps have the ability to raise low- Preheating Air or Water?
temperature energy to a higher temperature level. Due to the superior heat transfer qualities
The most common heat pump system is a closed of water, preheating feed water is more efficient
loop filled with refrigerant (Figure 12.20). and economical than preheating combustion air.
The heat pump cycle begins with a compres- However, air is always available at ambient tem-
sor raising the temperature of the working fluid, perature with good potential for accepting flue
in vapor form. This hot vapor goes to a heat ex- gas heat.
changer (condenser) where its heat is transferred
to heat air or water. The high pressure liquid re- Fire Tube Boiler Air Preheating
frigerant then passes through an expansion valve In general, fire tube boilers are not designed
and its pressure is suddenly lowered causing it to operate with preheated combustion air, and it
to cool. In the evaporator, this low temperature would be impractical to attempt to improve boil-
vapor absorbs energy from the waste heat stream er efficiency with this type of system.
raising its temperature. The refrigerant vapor