Page 43 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 43
28 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
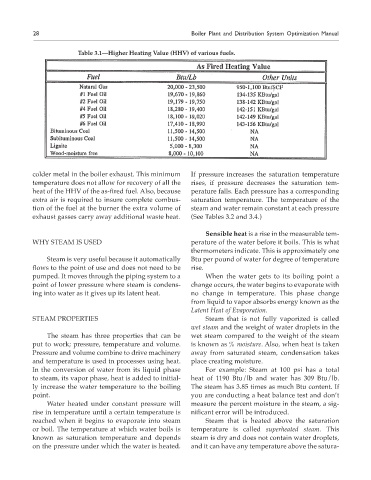
Table 3.1—Higher Heating value (HHv) of various fuels.
colder metal in the boiler exhaust. This minimum If pressure increases the saturation temperature
temperature does not allow for recovery of all the rises, if pressure decreases the saturation tem-
heat of the HHV of the as-fired fuel. Also, because perature falls. Each pressure has a corresponding
extra air is required to insure complete combus- saturation temperature. The temperature of the
tion of the fuel at the burner the extra volume of steam and water remain constant at each pressure
exhaust gasses carry away additional waste heat. (See Tables 3.2 and 3.4.)
Sensible heat is a rise in the measurable tem-
WHY STEAM IS USED perature of the water before it boils. This is what
thermometers indicate. This is approximately one
Steam is very useful because it automatically Btu per pound of water for degree of temperature
flows to the point of use and does not need to be rise.
pumped. It moves through the piping system to a When the water gets to its boiling point a
point of lower pressure where steam is condens- change occurs, the water begins to evaporate with
ing into water as it gives up its latent heat. no change in temperature. This phase change
from liquid to vapor absorbs energy known as the
Latent Heat of Evaporation.
STEAM PROPERTIES Steam that is not fully vaporized is called
wet steam and the weight of water droplets in the
The steam has three properties that can be wet steam compared to the weight of the steam
put to work; pressure, temperature and volume. is known as % moisture. Also, when heat is taken
Pressure and volume combine to drive machinery away from saturated steam, condensation takes
and temperature is used in processes using heat. place creating moisture.
In the conversion of water from its liquid phase For example: Steam at 100 psi has a total
to steam, its vapor phase, heat is added to initial- heat of 1190 Btu/lb and water has 309 Btu/lb.
ly increase the water temperature to the boiling The steam has 3.85 times as much Btu content. If
point. you are conducting a heat balance test and don’t
Water heated under constant pressure will measure the percent moisture in the steam, a sig-
rise in temperature until a certain temperature is nificant error will be introduced.
reached when it begins to evaporate into steam Steam that is heated above the saturation
or boil. The temperature at which water boils is temperature is called superheated steam. This
known as saturation temperature and depends steam is dry and does not contain water droplets,
on the pressure under which the water is heated. and it can have any temperature above the satura-