Page 75 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 75
60 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
• Insufficient flame turbulence or inadequate Use of the Smoke Tester,
mixing of fuel and air during the vaporiza- Three Simple Steps (Figure 7.2)
tion and burning. 1. Clamp the filter strip into the test pump and
insert into the flue.
These points are precisely why the smoke
2. Pump strokes.
test is an indispensable part of oil burner servic-
ing, accurate smoke testing takes less than a min- 3. Remove filter paper strip and place between
ute. smoke scale and white reflective and com-
pare smoke test spot on filter paper with
smoke spots on scale. The smoke reading is
THE SMOKE SPOT TEST the closest match.
Interpreting the Results
The smoke test method has long been recog-
Not all kinds of oil burners will be equally
nized as the acceptable standard for oil burners. It
affected by the same smoke content in the flue
is used by Underwriters Laboratories in approval
gas, this fact is shown in Figure 7.3 which inter-
testing of oil burners and it is the test method
prets smoke scale readings in terms of sooting
specified by the National Oil Fuel Institute and by
produced. Depending on the construction of the
the U.S. Department of Commerce, in their stan-
heat exchanger or the boiler, some units will ac-
dard for testing materials; (02156-65) and also in
cumulate soot rapidly with a number 3 smoke
the European standard DIN 51402.
spot number, while accumulation of soot on other
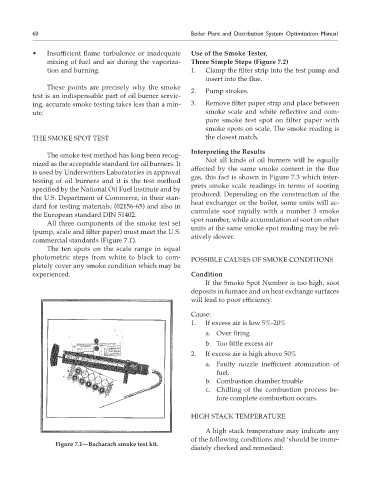
All three components of the smoke test set
units at the same smoke spot reading may be rel-
(pump, scale and filter paper) must meet the U.S.
atively slower.
commercial standards (Figure 7.1).
The ten spots on the scale range in equal
photometric steps from white to black to com- POSSIBLE CAUSES OF SMOKE CONDITIONS
pletely cover any smoke condition which may be
experienced. Condition
If the Smoke Spot Number is too high, soot
deposits in furnace and on heat exchange surfaces
will lead to poor efficiency.
Cause:
1. If excess air is low 5%-20%
a. Over firing
b. Too little excess air
2. If excess air is high above 50%
a. Faulty nozzle inefficient atomization of
fuel.
b. Combustion chamber trouble
c. Chilling of the combustion process be-
fore complete combustion occurs.
HIGH STACK TEMPERATURE
A high stack temperature may indicate any
of the following conditions and ‘should be imme-
Figure 7.1—Bacharach smoke test kit.
diately checked and remedied: