Page 66 - Bridge and Highway Structure Rehabilitation and Repair
P. 66
CHAPTER 2 DIAGNOSTIC DESIGN AND SELECTIVE RECONSTRUCTION 41
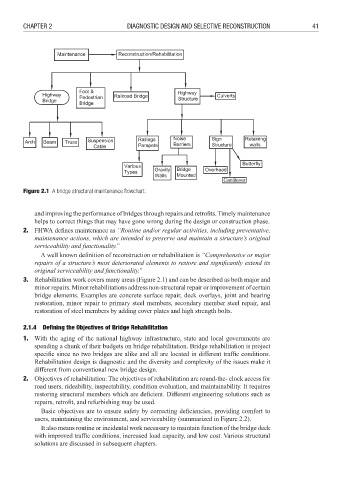
Figure 2.1 A bridge structural maintenance fl owchart.
and improving the performance of bridges through repairs and retrofi ts. Timely maintenance
helps to correct things that may have gone wrong during the design or construction phase.
2. FHWA defines maintenance as “Routine and/or regular activities, including preventative,
maintenance actions, which are intended to preserve and maintain a structure’s original
serviceability and functionality.”
A well known definition of reconstruction or rehabilitation is “Comprehensive or major
repairs of a structure’s most deteriorated elements to restore and signifi cantly extend its
original serviceability and functionality.”
3. Rehabilitation work covers many areas (Figure 2.1) and can be described as both major and
minor repairs. Minor rehabilitations address non-structural repair or improvement of certain
bridge elements. Examples are concrete surface repair, deck overlays, joint and bearing
restoration, minor repair to primary steel members, secondary member steel repair, and
restoration of steel members by adding cover plates and high strength bolts.
2.1.4 Defining the Objectives of Bridge Rehabilitation
1. With the aging of the national highway infrastructure, state and local governments are
spending a chunk of their budgets on bridge rehabilitation. Bridge rehabilitation is project
specific since no two bridges are alike and all are located in different traffi c conditions.
Rehabilitation design is diagnostic and the diversity and complexity of the issues make it
different from conventional new bridge design.
2. Objectives of rehabilitation: The objectives of rehabilitation are round-the- clock access for
road users, rideability, inspectability, condition evaluation, and maintainability. It requires
restoring structural members which are deficient. Different engineering solutions such as
repairs, retrofit, and refurbishing may be used.
Basic objectives are to ensure safety by correcting deficiencies, providing comfort to
users, maintaining the environment, and serviceability (summarized in Figure 2.2).
It also means routine or incidental work necessary to maintain function of the bridge deck
with improved traffi c conditions, increased load capacity, and low cost. Various structural
solutions are discussed in subsequent chapters.