Page 28 - Build Your Own Transistor Radios a Hobbyists Guide to High-Performance and Low-Powered Radio Circuits
P. 28
provides a low-frequency IF signal, which is amplified by the Q amplifier U3B. The
output of the Q amplifier provides a Ilow-frequency IF signal that is gO degrees out
of phase from the I channel amplifier's output.
Because the frequency of the IF signal is low, there is no need for special
high-speed operational amplifiers (op amps). Moderate-bandwidth (e.g., 10 MHz to
50 MHz) op amps are sufficient to provide amplification.
The local oscillator circuit that provides the 0- and gO-degree signals for the
quadrature mixer consists of a crystal oscillator and two flip-flop circuits. In a
typical operation, the OSCillator runs at four times the desired frequency for mixing,
and the two flip-flop circuits provide the one times frequency for mixing while also
generating 0- and gO-degree phase signals of the one times oscillator frequency.
The crystal oscillator consists of inverter gate U1A that serves as an amplifier bias
via RI . Low-pass-filter circuit R2 and C3 along with crystal Yi and C2 form a
three-stage phase-shifting network to provide 180 degrees of phase shift at
l
resonance or near resonance of the crystal, which a:lows for oscillation to occur at
the crystal's frequency.
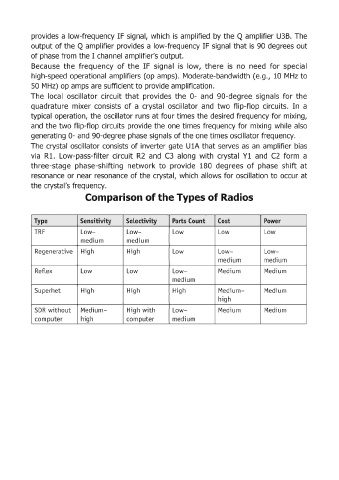
Comparison of the Types of Radios
Type Sensitivity Selectivity Parts Count Cost Power
TRF Low- Low- Low Low Low
medium medium
Regenerative High High Low Low- Low-
medium medium
Reflex Low Low Low- Medium Medium
medium
Superhet High High High Medium- Medium
high
SDR without Medium- High with Low- Medium Medium
computer high computer medium