Page 121 - Buried Pipe Design
P. 121
96 Chapter Three
deflection. Thus, when deflection calculations are based on the prism
load, the deflection lag factor D L should be 1.0.
Creep is normally associated with the pipe material and is defined
as continuing deformation with time when the material is subjected to
a constant load. Most plastics exhibit creep. As temperature increases,
the creep rate under a given load increases. Also, as stress increases,
the creep rate for a given temperature increases. Materials that creep
are also subject to stress relaxation. Stress relaxation is defined as the
decrease in stress, with time, in a material held in constant deforma-
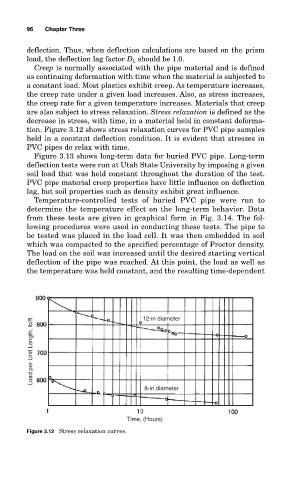
tion. Figure 3.12 shows stress relaxation curves for PVC pipe samples
held in a constant deflection condition. It is evident that stresses in
PVC pipes do relax with time.
Figure 3.13 shows long-term data for buried PVC pipe. Long-term
deflection tests were run at Utah State University by imposing a given
soil load that was held constant throughout the duration of the test.
PVC pipe material creep properties have little influence on deflection
lag, but soil properties such as density exhibit great influence.
Temperature-controlled tests of buried PVC pipe were run to
determine the temperature effect on the long-term behavior. Data
from these tests are given in graphical form in Fig. 3.14. The fol-
lowing procedures were used in conducting these tests. The pipe to
be tested was placed in the load cell. It was then embedded in soil
which was compacted to the specified percentage of Proctor density.
The load on the soil was increased until the desired starting vertical
deflection of the pipe was reached. At this point, the load as well as
the temperature was held constant, and the resulting time-dependent
Load per Unit Length, lb/ft 12-in diameter
8-in diameter
Time, (Hours)
Figure 3.12 Stress relaxation curves.