Page 73 - Business Plans that Work A Guide for Small Business
P. 73
64 • Business Plans that Work
This section provides
the basic parameters of the Business format franchisers are typically paid by
franchising industry. It should franchisees in three ways:
be noted that franchises are
sometimes categorized in
two ways; business format
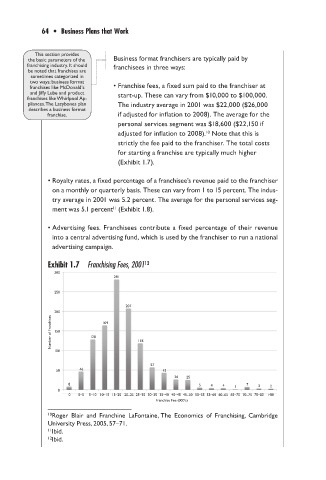
franchises like McDonald’s • Franchise fees, a fixed sum paid to the franchiser at
and Jiffy Lube and product start-up. These can vary from $10,000 to $100,000.
franchises like Whirlpool Ap-
pliances. The Lazybones plan The industry average in 2001 was $22,000 ($26,000
describes a business format
franchise. if adjusted for inflation to 2008). The average for the
personal services segment was $18,600 ($22,150 if
adjusted for inflation to 2008). Note that this is
10
strictly the fee paid to the franchiser. The total costs
for starting a franchise are typically much higher
(Exhibit 1.7).
• Royalty rates, a fixed percentage of a franchisee’s revenue paid to the franchiser
on a monthly or quarterly basis. These can vary from 1 to 15 percent. The indus-
try average in 2001 was 5.2 percent. The average for the personal services seg-
11
ment was 5.1 percent (Exhibit 1.8).
• Advertising fees. Franchisees contribute a fixed percentage of their revenue
into a central advertising fund, which is used by the franchiser to run a national
advertising campaign.
Exhibit 1.7 Franchising Fees, 2001 12
300
281
250
207
200
Number of Franchises 150 128 164 118
100
57
50 46 43
26 25
8 5 4 4 1 7 3 2
0
0 0–5 5–10 10–15 15–20 20–25 25–30 30–3535–40 40–45 45–50 50–5555–60 60–65 65–70 70–75 75–80 >80
Franchise Fee (000’s)
10 Roger Blair and Franchine LaFontaine, The Economics of Franchising, Cambridge
University Press, 2005, 57–71.
11 Ibid.
12 Ibid.