Page 37 - Calculus Demystified
P. 37
24
SOLUTION CHAPTER 1 Basics
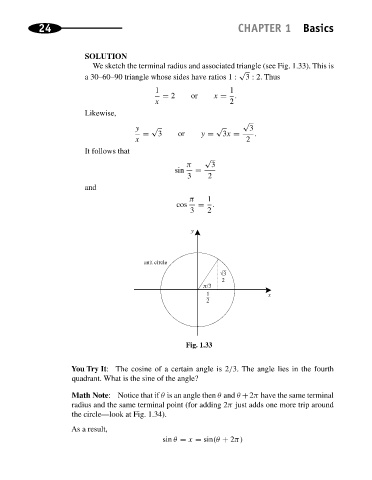
We sketch the terminal radius and associated triangle (see Fig. 1.33). This is
√
a 30–60–90 triangle whose sides have ratios 1 : 3 : 2. Thus
1 1
= 2 or x = .
x 2
Likewise,
√
y √ √ 3
= 3 or y = 3x = .
x 2
It follows that
√
π 3
sin =
3 2
and
π 1
cos = .
3 2
y
unit circle
√3
2
/3
1
x
2
Fig. 1.33
You Try It: The cosine of a certain angle is 2/3. The angle lies in the fourth
quadrant. What is the sine of the angle?
Math Note: Notice that if θ is an angle then θ and θ +2π have the same terminal
radius and the same terminal point (for adding 2π just adds one more trip around
the circle—look at Fig. 1.34).
As a result,
sin θ = x = sin(θ + 2π)