Page 226 - Caldera Volcanism Analysis, Modelling and Response
P. 226
Characterisation of Archean Subaqueous Calderas in Canada 201
D
Upper formational stage I
5 km
Incipient & Extensive e
Incipient & Extensiv
Incipient & Extensive
Carbonate and Oxide
Carbonate and Oxide
Carbonate and Oxide
Iron-formation
Activ
Active Subaqueous
Iron-formation
Iron-f or mation Active Subaqueous
e Subaqueous
Explosive Volcanism
e
Explosive Volcanism
V
olcanism
Explosiv
al Dome-flo
Centr
Central Dome-flow
Central Dome-flow w
complexes
complexes
comple x es
Mafic Flows
Mafic Flows
Mafic Flo ws
Hydrothermal
Hydrothermal
Hydrothermal
Activity
Activity
Activity
Sea le
Sea le
Sea level el el
v
v
Flanking
Flanking
Flanking
Satellite
Satellite
Satellite
Cones
Cones
Cones
Endogenous
Endogenous
Endogenous
Dome
Dome
ault
ault
F F
Fault Dome
Explosiv e dome
Explosiv
Explosive dome
e dome
collapse
collapse
collapse
Felsic
elsic
F Felsic
Dyke e
Dyke
Dyk
eeder
eeder
Swarm
Swarm
Sw ar m F F Feeder
es
Dykes
Dykes
Dyk
Caldera floor environments: dome flow complexes
with incipient mafic volcanism and alteration
E
Upper formational stage II
5 km
ucture
Cauldron Subsidence Str
Cauldron Subsidence Structure
Cauldron Subsidence Structure
Active Subaqueous
Active Subaqueous
Activ
e Subaqueous
Explosiv
Explosive Volcanism
Explosive Volcanism
olcanism
V
e
Central Dome
Centr al Dome Banded iron-f or or mation
Centr
Banded iron-f
Banded iron-formationmation
al Dome
Building
Building
Building
Incipient
Incipient
Incipient
Mafic Flows
Mafic Flo ws Hydrothermal
Mafic Flo
ws
Hydrother
mal
Hydrothermal
Sea level Activity
Activity
Activity
Flanking
Flanking
Flanking
Satellite
Satellite
Satellite
Cones
Cones
Cones
Breccia
Breccia
Breccia
Endogenous
Endogenous
Deposits Endogenous
Deposits
Deposits
Dome
Dome
Dome
ault
F Fault
Fault
F F Feeder
eeder
eeder
Dyke e Felsic
elsic
Dyk
Dyke
F Felsic
Feeder
eeder
System
System F Feeder
System
bro
Gab
Gab
bro
Gabbro Dyk es
Dykes
Dykes
Caldera floor environments: mafic volcanism and extensive
hydrothermal alteration
Figure 5 (Continued ).
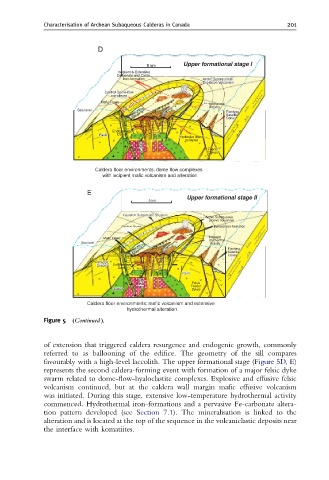
of extension that triggered caldera resurgence and endogenic growth, commonly
referred to as ballooning of the edifice. The geometry of the sill compares
favourably with a high-level laccolith. The upper formational stage (Figure 5D, E)
represents the second caldera-forming event with formation of a major felsic dyke
swarm related to dome-flow-hyaloclastite complexes. Explosive and effusive felsic
volcanism continued, but at the caldera wall margin mafic effusive volcanism
was initiated. During this stage, extensive low-temperature hydrothermal activity
commenced. Hydrothermal iron-formations and a pervasive Fe-carbonate altera-
tion pattern developed (see Section 7.1). The mineralisation is linked to the
alteration and is located at the top of the sequence in the volcaniclastic deposits near
the interface with komatiites.