Page 229 - Caldera Volcanism Analysis, Modelling and Response
P. 229
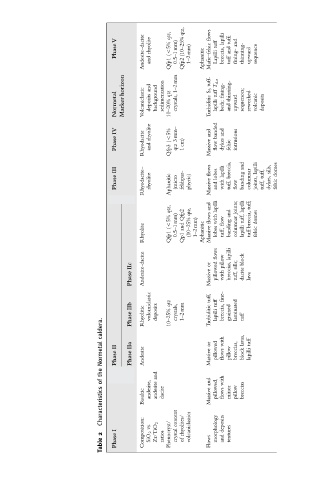
PhaseV Andesite–dacite rhyolite and qtz, (o5% Qfp1 0.5–1 mm) Qfp2 (10–25% qtz, 1–2 mm) Aphanitic flows Mafic–felsic tuff Lapilli lapilli breccia, tuff; and tuff and fining- thinning- upward sequence
Normetal Marker horizon Volcaniclastic and deposits background sedimentation qtz 10–20% crystals, 1–2 mm tuff- S 3 Turbiditic T d-e tuff lapilli fining- beds; thinning- and upward sequences; reworked volcanic deposits
IV rhyolite (o5% 3 mm– and banded and
Phase Rhyodacite and Qfp3 qtz 1 cm) Massive flow dykes felsic intrusions
III flows lobes lapilli breccia, and lapilli tuff, sills, domes
Phase Rhyodacite– rhyolite Aphanitic (micro feldspar- phyric) Massive and with tuff, flow banding columnar joints, tuff, dykes, felsic
qtz, Qfp2 qtz, and lapilli and joints; lapilli tuff;
(o5% 0.5–1 mm) and (10–25% 1–2 mm) flows with flow columnar tuff, breccia, domes
Rhyolite Qfp1 Qp1 Aphanitic Massive lobes tuff, banding lapilli tuff felsic
IIc Andesite-dacite or flows pillowed pillow lapilli breccias, sills; block
Phase Massive with tuff, dacite lava
IIb Rhyolitic volcaniclastic deposits qtz 10–25% crystals, 1–2 mm tuff, Turbiditic tuff lapilli fine- breccia, grained laminated tuff
caldera. Phase lavas,
Normetal II Phase IIa Phase Andesite or Massive pillowed with flows pillow breccias, block tuff lapilli
the and
of andesite, andesite dacite and pillowed, with flows minor pillow breccias
Characteristics Basaltic content Massive
I vs. rhyolites/ volcaniclastics morphology deposits
2 Composition: SiO 2 Zr/TiO 2 ratios Phenocryst/ crystal and textures
Table Phase of Flows