Page 32 - Caldera Volcanism Analysis, Modelling and Response
P. 32
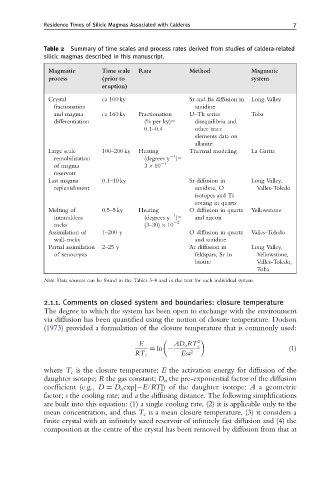
Residence Times of Silicic Magmas Associated with Calderas 7
Table 2 Summary of time scales and process rates derived from studies of caldera-related
silicic magmas described in this manuscript.
Magmatic Time scale Rate Method Magmatic
process (prior to system
eruption)
Crystal ca 100 ky Sr and Ba diffusion in Long Valley
fractionation sanidine
and magma ca 160 ky Fractionation U–Th series Toba
differentiation (% per ky)= disequilibria and
0.1–0.4 other trace
elements data on
allanite
Large scale 100–200 ky Heating Thermal modeling La Garita
1
remobilization (degrees y )=
of magma 3 10 4
reservoir
Last magma 0.1–10 ky Sr diffusion in Long Valley,
replenishment sanidine, O Valles-Toledo
isotopes and Ti
zoning in quartz
Melting of 0.5–5 ky Heating O diffusion in quartz Yellowstone
1
intracaldera (degrees y )= and zircon
rocks (3–30) 10 2
Assimilation of 1–200 y O diffusion in quartz Valles-Toledo
wall-rocks and sanidine
Partial assimilation 2–25 y Ar diffusion in Long Valley,
of xenocrysts feldspars, Sr in Yellowstone,
biotite Valles-Toledo,
Toba
Note: Data sources can be found in the Tables 3–8 and in the text for each individual system.
2.1.1. Comments on closed system and boundaries: closure temperature
The degree to which the system has been open to exchange with the environment
via diffusion has been quantified using the notion of closure temperature. Dodson
(1973) provided a formulation of the closure temperature that is commonly used:
E AD o RT 2 c
¼ ln 2 (1)
RT c Esa
where T c is the closure temperature; E the activation energy for diffusion of the
daughter isotope; R the gas constant; D o the pre-exponential factor of the diffusion
coefficient (e.g., D ¼ D o exp[ E/RT]) of the daughter isotope; A a geometric
factor; s the cooling rate; and a the diffusing distance. The following simplifications
are built into this equation: (1) a single cooling rate, (2) it is applicable only to the
mean concentration, and thus T c is a mean closure temperature, (3) it considers a
finite crystal with an infinitely sized reservoir of infinitely fast diffusion and (4) the
composition at the centre of the crystal has been removed by diffusion from that at