Page 103 - Cam Design Handbook
P. 103
THB4 8/15/03 1:01 PM Page 91
POLYNOMIAL AND FOURIER SERIES CAM CURVES 91
Displacement Dwell
Velocity
y, y', y"
Dwell Cam angle q
Acceleration
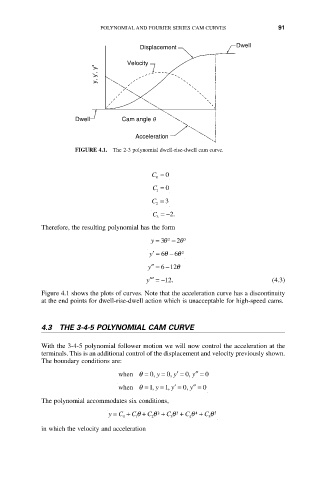
FIGURE 4.1. The 2-3 polynomial dwell-rise-dwell cam curve.
C = 0
0
C = 0
1
C = 3
2
C =- 2.
3
Therefore, the resulting polynomial has the form
y = 3q 2 - 2q 3
y ¢ = 6q - 6q 2
y ¢¢ =-612q
y ¢¢¢ =-12. (4.3)
Figure 4.1 shows the plots of curves. Note that the acceleration curve has a discontinuity
at the end points for dwell-rise-dwell action which is unacceptable for high-speed cams.
4.3 THE 3-4-5 POLYNOMIAL CAM CURVE
With the 3-4-5 polynomial follower motion we will now control the acceleration at the
terminals. This is an additional control of the displacement and velocity previously shown.
The boundary conditions are:
when q = 0, y = 0, y ¢ = 0, y ¢¢ = 0
when q =1, y =1, y ¢ = 0, y ¢¢ = 0
The polynomial accommodates six conditions,
y = C + C + C q 2 + C q 3 + C q 4 + C q 5
q
0 1 2 3 4 5
in which the velocity and acceleration