Page 104 - Cam Design Handbook
P. 104
THB4 8/15/03 1:01 PM Page 92
92 CAM DESIGN HANDBOOK
Displacement Dwell
y, y', y", y''' Velocity
Dwell
Jerk
Acceleration
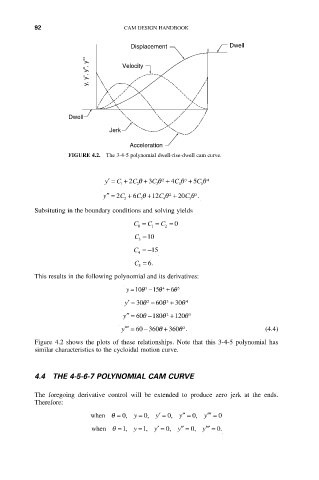
FIGURE 4.2. The 3-4-5 polynomial dwell-rise-dwell cam curve.
2
y ¢ = C + C q + C q 2 + C q 3 + C q 4
3
5
4
1 2 3 4 5
C
6
C
3
y ¢¢ = C2 2 + C q +12 q 2 + 20 q .
3
4
5
Subsituting in the boundary conditions and solving yields
C = C = C = 0
2
0
1
C = 10
3
C =- 15
4
C = 6.
5
This results in the following polynomial and its derivatives:
q
3
-
y =1015q 4 + 6q 5
2
y ¢ = 3060q 3 + 30q 4
-
q
-
q
y ¢¢ = 60180q 2 +120q 3
-
2
y ¢¢¢ = 60360q + 360q . (4.4)
Figure 4.2 shows the plots of these relationships. Note that this 3-4-5 polynomial has
similar characteristics to the cycloidal motion curve.
4.4 THE 4-5-6-7 POLYNOMIAL CAM CURVE
The foregoing derivative control will be extended to produce zero jerk at the ends.
Therefore:
when q = 0, y = 0, y ¢ = 0, y ¢¢ = 0, y ¢¢¢ = 0
when q =1, y =1, y ¢ = 0, y ¢¢ = 0, y ¢¢¢ = 0.