Page 113 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 113
Post-spinning treatments to carbon nanotube fibers 105
4.0E+04 8.0E–05
3.5E+04 7.0E–05
3.0E+04 6.0E–05
Conductivity (S/m) 2.5E+04 4.0E–05 Resistivity (Ωm)
5.0E–05
2.0E+04
3.0E–05
1.5E+04
1.0E+04 2.0E–05
5.0E+03 Conductivity Resistivity 1.0E–05
0.0E+00 0.0E+00
0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65 0.7 0.75 0.8
(A) Yarn porosity
600
Specific conductivity (S·cm 2 ·g –1 ) 400
500
300
200
100
0
0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
(B) CNT yarn porosity
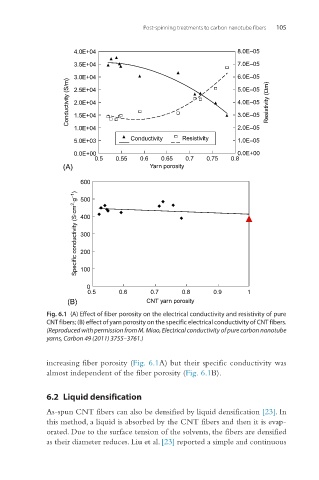
Fig. 6.1 (A) Effect of fiber porosity on the electrical conductivity and resistivity of pure
CNT fibers; (B) effect of yarn porosity on the specific electrical conductivity of CNT fibers.
(Reproduced with permission from M. Miao, Electrical conductivity of pure carbon nanotube
yarns, Carbon 49 (2011) 3755–3761.)
increasing fiber porosity (Fig. 6.1A) but their specific conductivity was
almost independent of the fiber porosity (Fig. 6.1B).
6.2 Liquid densification
As-spun CNT fibers can also be densified by liquid densification [23]. In
this method, a liquid is absorbed by the CNT fibers and then it is evap-
orated. Due to the surface tension of the solvents, the fibers are densified
as their diameter reduces. Liu et al. [23] reported a simple and continuous