Page 121 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 121
Post-spinning treatments to carbon nanotube fibers 113
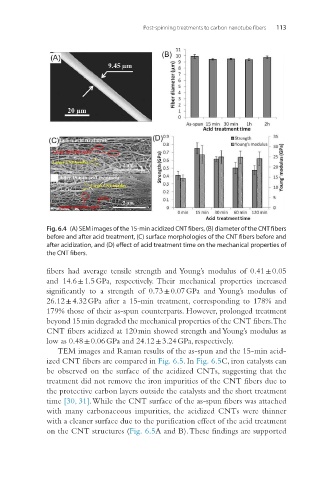
Fig. 6.4 (A) SEM images of the 15-min acidized CNT fibers, (B) diameter of the CNT fibers
before and after acid treatment, (C) surface morphologies of the CNT fibers before and
after acidization, and (D) effect of acid treatment time on the mechanical properties of
the CNT fibers.
fibers had average tensile strength and Young’s modulus of 0.41 ± 0.05
and 14.6 ± 1.5 GPa, respectively. Their mechanical properties increased
significantly to a strength of 0.73 ± 0.07 GPa and Young’s modulus of
26.12 ± 4.32 GPa after a 15-min treatment, corresponding to 178% and
179% those of their as-spun counterparts. However, prolonged treatment
beyond 15 min degraded the mechanical properties of the CNT fibers. The
CNT fibers acidized at 120 min showed strength and Young’s modulus as
low as 0.48 ± 0.06 GPa and 24.12 ± 3.24 GPa, respectively.
TEM images and Raman results of the as-spun and the 15-min acid-
ized CNT fibers are compared in Fig. 6.5. In Fig. 6.5C, iron catalysts can
be observed on the surface of the acidized CNTs, suggesting that the
treatment did not remove the iron impurities of the CNT fibers due to
the protective carbon layers outside the catalysts and the short treatment
time [30, 31]. While the CNT surface of the as-spun fibers was attached
with many carbonaceous impurities, the acidized CNTs were thinner
with a cleaner surface due to the purification effect of the acid treatment
on the CNT structures (Fig. 6.5A and B). These findings are supported