Page 122 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 122
114 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
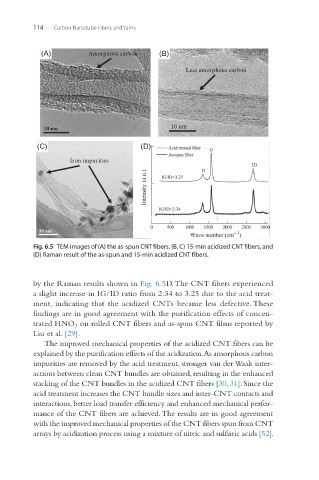
(A) Amorphous carbon (B)
Less amorphous carbon
10 nm
(C) (D)
Iron impurities
Fig. 6.5 TEM images of (A) the as-spun CNT fibers, (B, C) 15-min acidized CNT fibers, and
(D) Raman result of the as-spun and 15-min acidized CNT fibers.
by the Raman results shown in Fig. 6.5D. The CNT fibers experienced
a slight increase in IG/ID ratio from 2.34 to 3.25 due to the acid treat-
ment, indicating that the acidized CNTs became less defective. These
findings are in good agreement with the purification effects of concen-
trated HNO 3 on rolled CNT fibers and as-spun CNT films reported by
Liu et al. [29].
The improved mechanical properties of the acidized CNT fibers can be
explained by the purification effects of the acidization. As amorphous carbon
impurities are removed by the acid treatment, stronger van der Waals inter-
actions between clean CNT bundles are obtained, resulting in the enhanced
stacking of the CNT bundles in the acidized CNT fibers [30, 31]. Since the
acid treatment increases the CNT bundle sizes and inter-CNT contacts and
interactions, better load transfer efficiency and enhanced mechanical perfor-
mance of the CNT fibers are achieved. The results are in good agreement
with the improved mechanical properties of the CNT fibers spun from CNT
arrays by acidization process using a mixture of nitric and sulfuric acids [52].