Page 147 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 147
140 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
(A) (B)
(C) (D)
1.2 9
8 7
Relative yarn diameter (d/D) 0.8 Low twist yarn Poisson’s ratio 6 5 4 3 Low twist yarn
1
0.6
High twist yarn
0.4
High twist yarn
0.2
0 2 1 0
0 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.1 0 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.1
(E) Axial strain (F) Axial strain
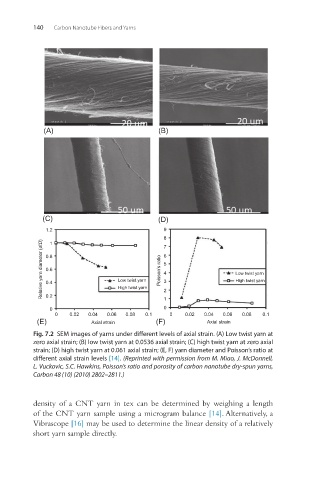
Fig. 7.2 SEM images of yarns under different levels of axial strain. (A) Low twist yarn at
zero axial strain; (B) low twist yarn at 0.0536 axial strain; (C) high twist yarn at zero axial
strain; (D) high twist yarn at 0.061 axial strain; (E, F) yarn diameter and Poisson’s ratio at
different axial strain levels [14]. (Reprinted with permission from M. Miao, J. McDonnell,
L. Vuckovic, S.C. Hawkins, Poisson’s ratio and porosity of carbon nanotube dry-spun yarns,
Carbon 48 (10) (2010) 2802–2811.)
density of a CNT yarn in tex can be determined by weighing a length
of the CNT yarn sample using a microgram balance [14]. Alternatively, a
Vibrascope [16] may be used to determine the linear density of a relatively
short yarn sample directly.