Page 161 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 161
152 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
resin, resulting in a CNT nanocomposite material [34–38]. In some cases,
the polymer matrix may be removed after the alignment treatment to ob-
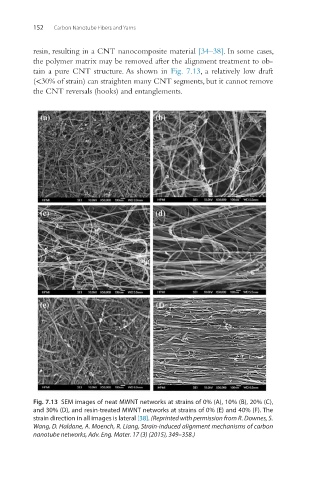
tain a pure CNT structure. As shown in Fig. 7.13, a relatively low draft
(<30% of strain) can straighten many CNT segments, but it cannot remove
the CNT reversals (hooks) and entanglements.
Fig. 7.13 SEM images of neat MWNT networks at strains of 0% (A), 10% (B), 20% (C),
and 30% (D), and resin-treated MWNT networks at strains of 0% (E) and 40% (F). The
strain direction in all images is lateral [38]. (Reprinted with permission from R. Downes, S.
Wang, D. Haldane, A. Moench, R. Liang, Strain‐induced alignment mechanisms of carbon
nanotube networks, Adv. Eng. Mater. 17 (3) (2015), 349–358.)