Page 175 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 175
166 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
2000 800
Conductivity
Strength 600
Average strength (MPa) 1000 400 Electrical conducitivity (S/cm)
1500
500
200
0 0
NMP
Water
(A) Dry-spun Cyclohexane Styrene Glycerin Ethanol Ethylene glycol Acetone DMF DMSO
Toluene
n-Hexane
Methanol
Acetonitrile
Ethyl acetate
Cyclohexene
1,3–propanediol
3.0
Specific strength (N/tex) 1.8
2.4
1.2
0.6
0.0
(B) Pristine NMP0%NMP7%CSA0%CSA7%CSA13%
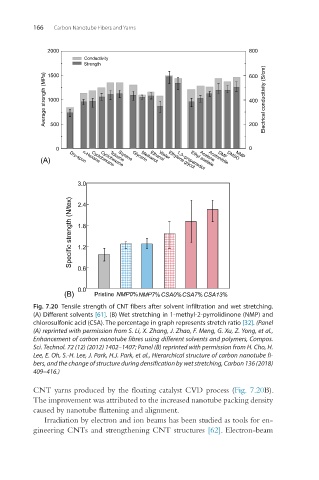
Fig. 7.20 Tensile strength of CNT fibers after solvent infiltration and wet stretching.
(A) Different solvents [61]. (B) Wet stretching in 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (NMP) and
chlorosulfonic acid (CSA). The percentage in graph represents stretch ratio [32]. (Panel
(A) reprinted with permission from S. Li, X. Zhang, J. Zhao, F. Meng, G. Xu, Z. Yong, et al.,
Enhancement of carbon nanotube fibres using different solvents and polymers, Compos.
Sci. Technol. 72 (12) (2012) 1402–1407; Panel (B) reprinted with permission from H. Cho, H.
Lee, E. Oh, S.-H. Lee, J. Park, H.J. Park, et al., Hierarchical structure of carbon nanotube fi-
bers, and the change of structure during densification by wet stretching, Carbon 136 (2018)
409–416.)
CNT yarns produced by the floating catalyst CVD process (Fig. 7.20B).
The improvement was attributed to the increased nanotube packing density
caused by nanotube flattening and alignment.
Irradiation by electron and ion beams has been studied as tools for en-
gineering CNTs and strengthening CNT structures [62]. Electron-beam