Page 181 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 181
172 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
4 3 y =4.3148x+ 0.103 4 6 5
Conductivity (×10 4 S/m) 2 1 R =0.9571 Conductivity (×10 4 S/m) 3 2 Conductivity 4 3 2 Specific conductivity (×10 4 S•m/tex)
2
y=0.0035x+4.2412
2
R =0.0529
0 1 0 Specific conductivity 1 0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 0 10 20 30 40 50 60
(A) Yarn density (g/cm ) 3 (B) Twist angle (degrees)
8 7 8 7
Conductivity (×10 4 S/m) 6 5 4 3 2 Twisted Specific conductivity (×10 4 S.m/tex) 6 5 4 3 Twisted
0 1 False-twisted 2 1 0 False-twisted
0 5 10 15 20 25 0 5 10 15 20 25
(C) Twist/false-twist (×10 T/m) (D) Twist/false-twist (×10 T/m)
3
3
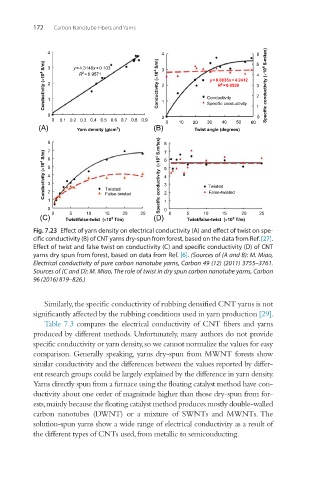
Fig. 7.23 Effect of yarn density on electrical conductivity (A) and effect of twist on spe-
cific conductivity (B) of CNT yarns dry-spun from forest, based on the data from Ref. [27].
Effect of twist and false twist on conductivity (C) and specific conductivity (D) of CNT
yarns dry spun from forest, based on data from Ref. [6]. (Sources of (A and B): M. Miao,
Electrical conductivity of pure carbon nanotube yarns, Carbon 49 (12) (2011) 3755–3761.
Sources of (C and D): M. Miao, The role of twist in dry spun carbon nanotube yarns, Carbon
96 (2016) 819–826.)
Similarly, the specific conductivity of rubbing densified CNT yarns is not
significantly affected by the rubbing conditions used in yarn production [29].
Table 7.3 compares the electrical conductivity of CNT fibers and yarns
produced by different methods. Unfortunately, many authors do not provide
specific conductivity or yarn density, so we cannot normalize the values for easy
comparison. Generally speaking, yarns dry-spun from MWNT forests show
similar conductivity and the differences between the values reported by differ-
ent research groups could be largely explained by the difference in yarn density.
Yarns directly spun from a furnace using the floating catalyst method have con-
ductivity about one order of magnitude higher than those dry-spun from for-
ests, mainly because the floating catalyst method produces mostly double-walled
carbon nanotubes (DWNT) or a mixture of SWNTs and MWNTs. The
solution-spun yarns show a wide range of electrical conductivity as a result of
the different types of CNTs used, from metallic to semiconducting.