Page 182 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 182
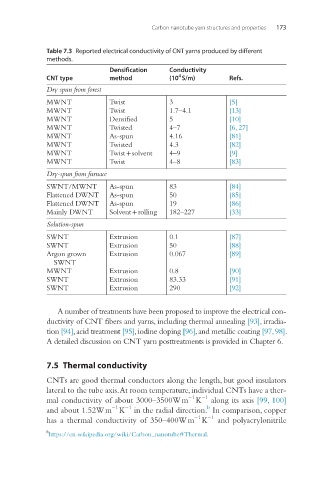
Carbon nanotube yarn structures and properties 173
Table 7.3 Reported electrical conductivity of CNT yarns produced by different
methods.
Densification Conductivity
4
CNT type method (10 S/m) Refs.
Dry spun from forest
MWNT Twist 3 [5]
MWNT Twist 1.7–4.1 [13]
MWNT Densified 5 [10]
MWNT Twisted 4–7 [6, 27]
MWNT As-spun 4.16 [81]
MWNT Twisted 4.3 [82]
MWNT Twist + solvent 4–9 [9]
MWNT Twist 4–8 [83]
Dry-spun from furnace
SWNT/MWNT As-spun 83 [84]
Flattened DWNT As-spun 50 [85]
Flattened DWNT As-spun 19 [86]
Mainly DWNT Solvent + rolling 182–227 [33]
Solution-spun
SWNT Extrusion 0.1 [87]
SWNT Extrusion 50 [88]
Argon grown Extrusion 0.067 [89]
SWNT
MWNT Extrusion 0.8 [90]
SWNT Extrusion 83.33 [91]
SWNT Extrusion 290 [92]
A number of treatments have been proposed to improve the electrical con-
ductivity of CNT fibers and yarns, including thermal annealing [93], irradia-
tion [94], acid treatment [95], iodine doping [96], and metallic coating [97, 98].
A detailed discussion on CNT yarn posttreatments is provided in Chapter 6.
7.5 Thermal conductivity
CNTs are good thermal conductors along the length, but good insulators
lateral to the tube axis. At room temperature, individual CNTs have a ther-
−1
−1
mal conductivity of about 3000–3500 W m K along its axis [99, 100]
b
−1
−1
and about 1.52 W m K in the radial direction. In comparison, copper
−1
−1
has a thermal conductivity of 350–400 W m K and polyacrylonitrile
b https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_nanotube#Thermal.