Page 201 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 201
Mechanics modeling of carbon nanotube yarns 191
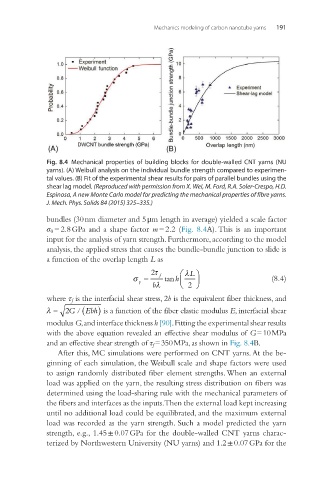
Fig. 8.4 Mechanical properties of building blocks for double-walled CNT yarns (NU
yarns). (A) Weibull analysis on the individual bundle strength compared to experimen-
tal values. (B) Fit of the experimental shear results for pairs of parallel bundles using the
shear lag model. (Reproduced with permission from X. Wei, M. Ford, R.A. Soler-Crespo, H.D.
Espinosa, A new Monte Carlo model for predicting the mechanical properties of fibre yarns.
J. Mech. Phys. Solids 84 (2015) 325–335.)
bundles (30 nm diameter and 5 μm length in average) yielded a scale factor
σ 0 = 2.8 GPa and a shape factor m = 2.2 (Fig. 8.4A). This is an important
input for the analysis of yarn strength. Furthermore, according to the model
analysis, the applied stress that causes the bundle-bundle junction to slide is
a function of the overlap length L as
τ 2 λL
σ = f tan h (8.4)
y
λ b 2
where τ f is the interfacial shear stress, 2b is the equivalent fiber thickness, and
λ = 2G / (Ebh ) is a function of the fiber elastic modulus E, interfacial shear
modulus G, and interface thickness h [90]. Fitting the experimental shear results
with the above equation revealed an effective shear modulus of G = 10 MPa
and an effective shear strength of τ f = 350 MPa, as shown in Fig. 8.4B.
After this, MC simulations were performed on CNT yarns. At the be-
ginning of each simulation, the Weibull scale and shape factors were used
to assign randomly distributed fiber element strengths. When an external
load was applied on the yarn, the resulting stress distribution on fibers was
determined using the load-sharing rule with the mechanical parameters of
the fibers and interfaces as the inputs. Then the external load kept increasing
until no additional load could be equilibrated, and the maximum external
load was recorded as the yarn strength. Such a model predicted the yarn
strength, e.g., 1.45 ± 0.07 GPa for the double-walled CNT yarns charac-
terized by Northwestern University (NU yarns) and 1.2 ± 0.07 GPa for the