Page 67 - Carbonate Sedimentology and Sequence Stratigraphy
P. 67
58 WOLFGANG SCHLAGER
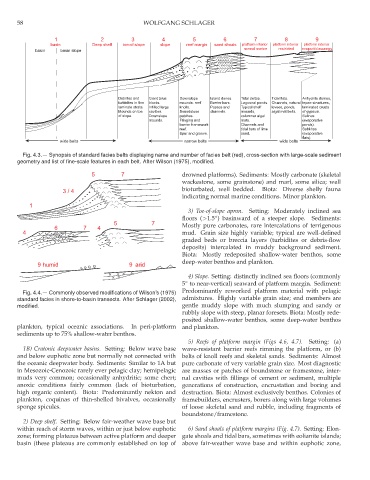
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
basin Deep shelf toe-of-slope slope reef margin sand shoals platform interior platform interior platform interior
normal marine restricted evaporitic\swampy
basin basin slope
Debrites and Giant talus Downslope Island dunes. Tidal deltas. Tidal flats. Anhydrite domes,
turbidites in fine blocks. mounds. reef Barrier bars. Lagoonal ponds. Channels, natural tepee structures,
laminate strata. Infilled large knolls. Passes and Typical shelf levees, ponds, laminated crusts
Mounds on toe cavities. Boundstone channels. mounds, algal mat belts. of gypsum.
of slope. Downslope patches. columnar algal Salinas
mounds. Fringing and mats. (evaporative
barrier framework Channels and ponds).
reef. tidal bars of lime Sabkhas
Spur and groove. sand. (evaporative
flats).
wide belts narrow belts wide belts
Fig. 4.3.— Synopsis of standard facies belts displaying name and number of facies belt (red), cross-section with large-scale sediment
geometry and list of fine-scale features in each belt. After Wilson (1975), modified.
5 7 drowned platforms). Sediments: Mostly carbonate (skeletal
wackestone, some grainstone) and marl, some silica; well
bioturbated, well bedded. Biota: Diverse shelly fauna
3 / 4
indicating normal marine conditions. Minor plankton.
1
3) Toe-of-slope apron. Setting: Moderately inclined sea
◦
floors (>1.5 ) basinward of a steeper slope. Sediments:
5 7 Mostly pure carbonates, rare intercalations of terrigenous
6 7 4
4 mud. Grain size highly variable; typical are well-defined
graded beds or breccia layers (turbidites or debris-flow
deposits) intercalated in muddy background sediment.
Biota: Mostly redeposited shallow-water benthos, some
deep-water benthos and plankton.
9 humid 9 arid
4) Slope. Setting: distinctly inclined sea floors (commonly
◦
5 to near-vertical) seaward of platform margin. Sediment:
Fig. 4.4.— Commonly observed modifications of Wilson’s (1975) Predominantly reworked platform material with pelagic
standard facies in shore-to-basin transects. After Schlager (2002), admixtures. Highly variable grain size; end members are
modified. gentle muddy slope with much slumping and sandy or
rubbly slope with steep, planar foresets. Biota: Mostly rede-
posited shallow-water benthos, some deep-water benthos
plankton, typical oceanic associations. In peri-platform and plankton.
sediments up to 75% shallow-water benthos.
5) Reefs of platform margin (Figs 4.6, 4.7). Setting: (a)
1B) Cratonic deepwater basins. Setting: Below wave base wave-resistant barrier reefs rimming the platform, or (b)
and below euphotic zone but normally not connected with belts of knoll reefs and skeletal sands. Sediments: Almost
the oceanic deepwater body. Sediments: Similar to 1A but pure carbonate of very variable grain size. Most diagnostic
in Mesozoic-Cenozoic rarely ever pelagic clay; hemipelagic are masses or patches of boundstone or framestone, inter-
muds very common; occasionally anhydritic; some chert; nal cavities with fillings of cement or sediment, multiple
anoxic conditions fairly common (lack of bioturbation, generations of construction, encrustation and boring and
high organic content). Biota: Predominantly nekton and destruction. Biota: Almost exclusively benthos. Colonies of
plankton, coquinas of thin-shelled bivalves, occasionally framebuilders, encrusters, borers along with large volumes
sponge spicules. of loose skeletal sand and rubble, including fragments of
boundstone/framestone.
2) Deep shelf. Setting: Below fair-weather wave base but
within reach of storm waves, within or just below euphotic 6) Sand shoals of platform margins (Fig. 4.7). Setting: Elon-
zone; forming plateaus between active platform and deeper gate shoals and tidal bars, sometimes with eolianite islands;
basin (these plateaus are commonly established on top of above fair-weather wave base and within euphotic zone,