Page 437 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 437
400 Carraher’s Polymer Chemistry
R
R
R
R
O S O O S O
Na +
OH OH
R
R
O S O O S O
− + 2+ + − +
O Na Mg Na O Na
R
R
O S O O S O
O O
Mg
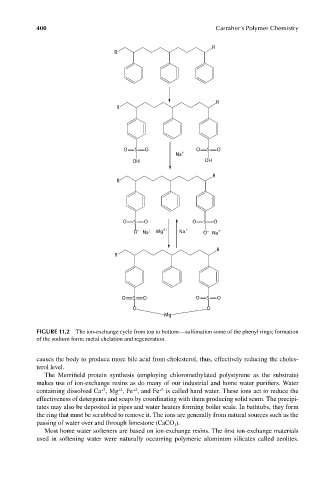
FIGURE 11.2 The ion-exchange cycle from top to bottom—sulfonation some of the phenyl rings; formation
of the sodium form; metal chelation and regeneration.
causes the body to produce more bile acid from cholesterol, thus, effectively reducing the choles-
terol level.
The Merrifield protein synthesis (employing chloromethylated polystyrene as the substrate)
makes use of ion-exchange resins as do many of our industrial and home water purifi ers. Water
+3
+2
containing dissolved Ca , Mg , Fe , and Fe is called hard water. These ions act to reduce the
+2
+2
effectiveness of detergents and soaps by coordinating with them producing solid scum. The precipi-
tates may also be deposited in pipes and water heaters forming boiler scale. In bathtubs, they form
the ring that must be scrubbed to remove it. The ions are generally from natural sources such as the
passing of water over and through limestone (CaCO ).
3
Most home water softeners are based on ion-exchange resins. The first ion-exchange materials
used in softening water were naturally occurring polymeric aluminum silicates called zeolites.
9/14/2010 3:41:46 PM
K10478.indb 400
K10478.indb 400 9/14/2010 3:41:46 PM