Page 537 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 537
500 Carraher’s Polymer Chemistry
Applied force
Indenter
A
B
Test material
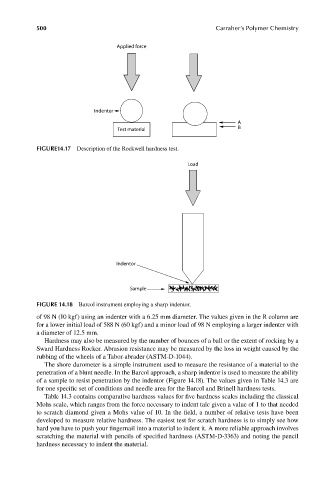
FIGURE14.17 Description of the Rockwell hardness test.
Load
Indentor
Sample
FIGURE 14.18 Barcol instrument employing a sharp indentor.
of 98 N (10 kgf) using an indenter with a 6.25 mm diameter. The values given in the R column are
for a lower initial load of 588 N (60 kgf) and a minor load of 98 N employing a larger indenter with
a diameter of 12.5 mm.
Hardness may also be measured by the number of bounces of a ball or the extent of rocking by a
Sward Hardness Rocker. Abrasion resistance may be measured by the loss in weight caused by the
rubbing of the wheels of a Tabor-abrader (ASTM-D-1044).
The shore durometer is a simple instrument used to measure the resistance of a material to the
penetration of a blunt needle. In the Barcol approach, a sharp indentor is used to measure the ability
of a sample to resist penetration by the indentor (Figure 14.18). The values given in Table 14.3 are
for one specific set of conditions and needle area for the Barcol and Brinell hardness tests.
Table 14.3 contains comparative hardness values for fi ve hardness scales including the classical
Mohs scale, which ranges from the force necessary to indent talc given a value of 1 to that needed
to scratch diamond given a Mohs value of 10. In the field, a number of relative tests have been
developed to measure relative hardness. The easiest test for scratch hardness is to simply see how
hard you have to push your fingernail into a material to indent it. A more reliable approach involves
scratching the material with pencils of specified hardness (ASTM-D-3363) and noting the pencil
hardness necessary to indent the material.
9/14/2010 3:42:42 PM
K10478.indb 500 9/14/2010 3:42:42 PM
K10478.indb 500