Page 660 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 660
Selected Topics 623
Complex formation is important in photophysics. Two terms need to be described here. First,
an exciplex is an excited state complex formed between two different kinds of molecules, one that
is excited and the other that is in its grown state. The second term, excimer, is similar except the
complex is formed between like molecules. Here we will focus on excimer complexes that form
between two like polymer chains or within the same polymer chain. Such complexes are often
formed between two aromatic structures. Resonance interactions between aromatic structures, such
as two phenyl rings in polystyrene (PS), give a weak intermolecular force formed from attractions
between the pi electrons of the two aromatic entities. Excimers involving such aromatic structures
give strong fl uorescence.
Excimer formation can be described as follows where [PP]* is the excimer:
P* + P → [PP]* (19.22)
The excimer decays giving two ground state aromatic sites and emission of fl uorescence.
[PP]* → hν + 2P (19.23)
As always, the energy of the light emitted is less than that originally taken on. By studying the
amount and energy of the fluorescence radiation decay rates, depolarization effects, excimer stabil-
ity, and structure can be determined.
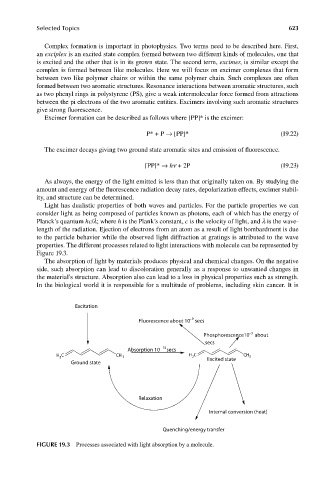
Light has dualistic properties of both waves and particles. For the particle properties we can
consider light as being composed of particles known as photons, each of which has the energy of
Planck’s quantum hc/λ; where h is the Plank’s constant, c is the velocity of light, and λ is the wave-
length of the radiation. Ejection of electrons from an atom as a result of light bombardment is due
to the particle behavior while the observed light diffraction at gratings is attributed to the wave
properties. The different processes related to light interactions with molecule can be represented by
Figure 19.3.
The absorption of light by materials produces physical and chemical changes. On the negative
side, such absorption can lead to discoloration generally as a response to unwanted changes in
the material’s structure. Absorption also can lead to a loss in physical properties such as strength.
In the biological world it is responsible for a multitude of problems, including skin cancer. It is
Excitation
–9
Fluorescence about 10 secs
–3
Phosphorescence10 about
secs
–15
Absorption 10 secs
H C CH 3 H C CH 3
2 2 Excited state
Ground state
Relaxation
Internal conversion (heat)
Quenching/energy transfer
FIGURE 19.3 Processes associated with light absorption by a molecule.
9/14/2010 3:43:51 PM
K10478.indb 623 9/14/2010 3:43:51 PM
K10478.indb 623