Page 108 - Catalysts for Fine Chemical Synthesis Vol 1 - Robert & Poignant
P. 108
94 hydrolysis, oxidation and reduction
6.2 ASYMMETRIC EPOXIDATION OF DISUBSTITUTED E-ALKENES
USING A D-FRUCTOSE BASED CATALYST [2]
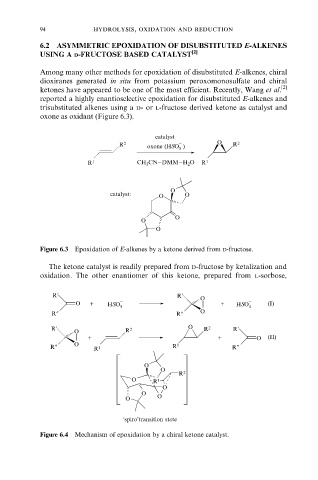
Among many other methods for epoxidation of disubstituted E-alkenes, chiral
dioxiranes generated in situ from potassium peroxomonosulfate and chiral
ketones have appeared to be one of the most efficient. Recently, Wang et al. [2]
reported a highly enantioselective epoxidation for disubstituted E-alkenes and
trisubstituted alkenes using a d- or l-fructose derived ketone as catalyst and
oxone as oxidant (Figure 6.3).
catalyst
−
R 2 oxone (HSO ) O R 2
5
R 1 CH 3 CN−DMM−H 2 O R 1
O
catalyst: O O
O
O
O
Figure 6.3 Epoxidation of E-alkenes by a ketone derived from d-fructose.
The ketone catalyst is readily prepared from d-fructose by ketalization and
oxidation. The other enantiomer of this ketone, prepared from l-sorbose,
R9 R9
− O −
O + HSO 5 + HSO 4 (I)
R99 R99 O
R9 R 2 O R 2 R9
O
+ + O (II)
O
R99 R 1 R 1 R99
O
O
R 2
O R 1
O
O O
O
‘spiro’transition state
Figure 6.4 Mechanism of epoxidation by a chiral ketone catalyst.