Page 278 - Centrifugal Pumps Design and Application
P. 278
Hydraulic Power Recovery Turbines 247
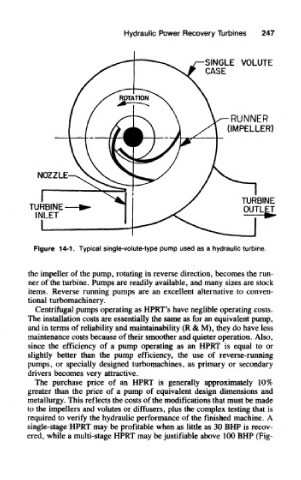
Figure 14-1. Typical single-volute-type pump used as a hydraulic turbine,
the impeller of the pump, rotating in reverse direction, becomes the run-
ner of the turbine. Pumps are readily available, and many sizes are stock
items. Reverse running pumps are an excellent alternative to conven-
tional turbomachinery.
Centrifugal pumps operating as HPRT's have neglible operating costs.
The installation costs are essentially the same as for an equivalent pump,
and in terms of reliability and maintainability (R & M), they do have less
maintenance costs because of their smoother and quieter operation. Also,
since the efficiency of a pump operating as an HPRT is equal to or
slightly better than the pump efficiency, the use of reverse-running
pumps, or specially designed turbomachines, as primary or secondary
drivers becomes very attractive.
The purchase price of an HPRT is generally approximately 10%
greater than the price of a pump of equivalent design dimensions and
metallurgy. This reflects the costs of the modifications that must be made
to the impellers and volutes or diffusers, plus the complex testing that is
required to verify the hydraulic performance of the finished machine. A
single-stage HPRT may be profitable when as little as 30 BHP is recov-
ered, while a multi-stage HPRT may be justifiable above 100 BHP (Fig-